Data Integrity
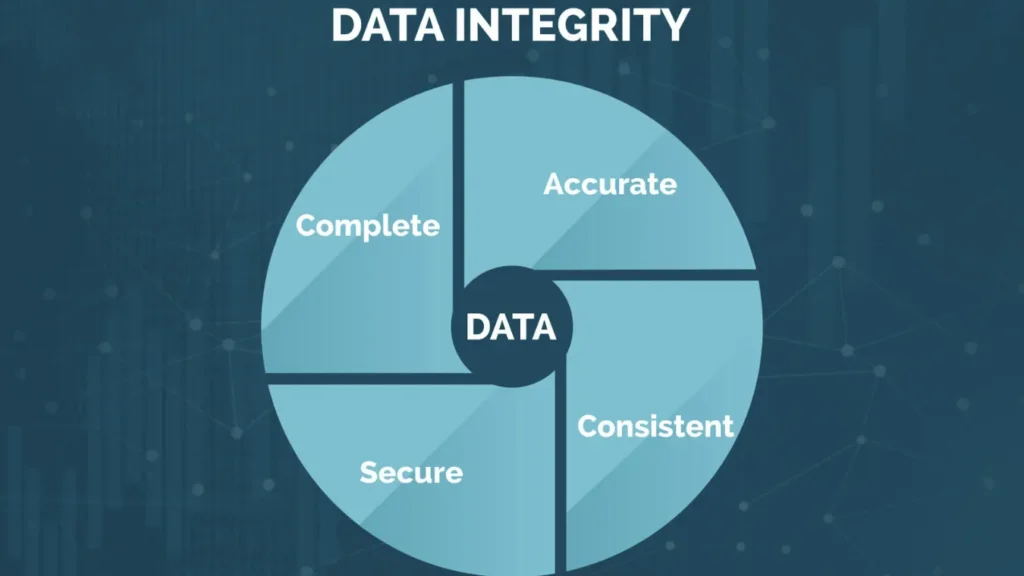
Table of Contents
Table of Contents
Real Consequences When Data Integrity Fails
Numbers can look correct on the screen while quietly drifting away from reality.
A single flipped bit in storage, a broken join in a report, or a half-finished write during a crash can change decisions, invoices, or audit results.
Data integrity focuses on these risks.
It ensures that stored and transmitted data remains accurate, consistent, and trustworthy over its entire lifecycle.

Dimensions of Data Integrity
Data integrity covers more than simple “no corruption.”
Several dimensions work together.
First, physical integrity deals with bit-level correctness on disks, SSDs, and networks.
Second, logical integrity ensures that relationships between records still follow business rules.
Third, temporal integrity checks that values make sense over time.
Finally, audit integrity tracks who changed what and when.
Because all four interact, a weakness in any one area can undermine the rest.
Mechanisms That Protect Data in Motion and at Rest
Systems defend integrity at many layers.
Storage devices use checksums, parity, and error-correcting codes to detect or repair bit flips.
File systems add their own checks and journaling.
Transport protocols such as TCP include sequence numbers and checksums to keep streams complete and ordered.
Additionally, applications apply validation rules before they accept or modify records.
When each layer enforces its part, the whole stack resists silent corruption much more effectively.
Data Integrity in Databases and SQL
Relational databases offer powerful tools for logical integrity.
They enforce structure, relationships, and allowed values through schema design and constraints.
Important features include:
Strong data types for each column
Primary keys that uniquely identify rows
Foreign keys that maintain relationships
CHECK constraints for ranges and formats
UNIQUE constraints to avoid duplicate identifiers
Furthermore, SQL transactions group changes into atomic units.
Either the entire change set commits or the engine rolls it back, which keeps sets of related updates internally consistent.
Integrity in Backup, Restore, and Recovery
Backups that restore successfully but contain silent corruption still fail the real test.
Therefore, integrity must extend into every backup and recovery workflow.
Good practice includes:
Verifying backup files with checksums or hash comparisons
Testing restores on non-production systems regularly
Tracking backup job metadata so you can trace specific runs
When something goes wrong and volumes turn RAW or files disappear, Amagicsoft Data Recovery helps reconstruct data from damaged media.
However, long-term trust still depends on backups and validation, not recovery alone.
Supports Windows 7/8/10/11 and Windows Server.
Supports Windows 7/8/10/11 and Windows Server
Practical Steps to Strengthen Data Integrity
Improving integrity does not always require new products.
It often starts with clearer rules and disciplined habits.
Recommended steps:
Define what “correct data” means for each critical field
Use the strongest appropriate data types instead of generic strings
Apply validation at the UI, API, and database levels
Keep schema changes versioned, reviewed, and tested
Use role-based access control to limit who can update sensitive records
In addition, you should align these steps with incident response plans so teams know how to react when checks start failing.
Monitoring and Integrity Checks in Daily Operation
Integrity does not stay guaranteed after deployment; you must keep checking.
Regular monitoring catches problems before they spread.
Useful techniques:
Scheduled queries that compare counts, totals, and balances across systems
Hash-based comparisons between source and target tables after ETL jobs
File integrity monitoring for critical configuration and binary files
Log review for repeated validation errors or failed writes
As a result, you get early warnings instead of discovering issues during audits or customer complaints.
Conclusion
Data integrity turns raw storage into reliable information.
It aligns physical protection, logical constraints, and ongoing verification so data stays accurate and consistent from entry to archive.
When failures occur, careful recovery with tools such as Amagicsoft Data Recovery can rescue content from damaged disks.
Yet the strongest position comes from prevention: well-designed schemas, disciplined validation, and continuous integrity checks.
Supports Windows 7/8/10/11 and Windows Server
FAQ
What is meant by data integrity?
What are the 4 types of data integrity?
How do you ensure data integrity?
What is integrity of data in SQL?
What are the 7 principles of data integrity?
What are the two concepts of integrity?
What are the 4 types of integrity constraints?
What are the three rules of data integrity?
How do you check data integrity?
Eddie is an IT specialist with over 10 years of experience working at several well-known companies in the computer industry. He brings deep technical knowledge and practical problem-solving skills to every project.