Data Link Layer
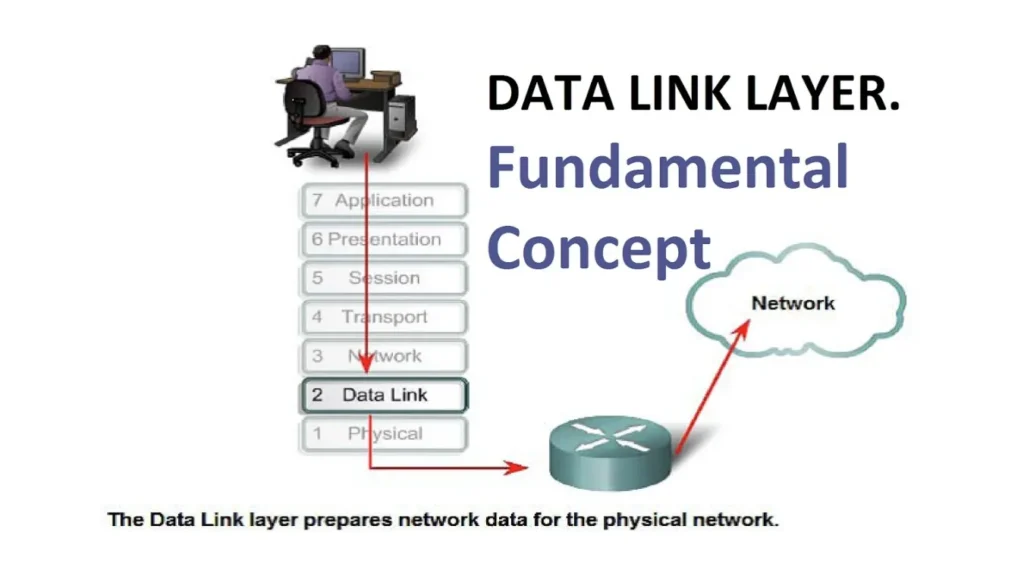
Table of Contents
First Hop: Where Devices Actually Meet
When two devices share a cable or a Wi-Fi access point, they first talk at the data link layer.
This layer wraps raw bits from the physical layer into frames, adds local addresses, and coordinates who can speak next.
As a result, the data link layer turns an unreliable electrical medium into a manageable local channel.
Upper layers can then focus on routing, sessions, and applications instead of collisions and noise.
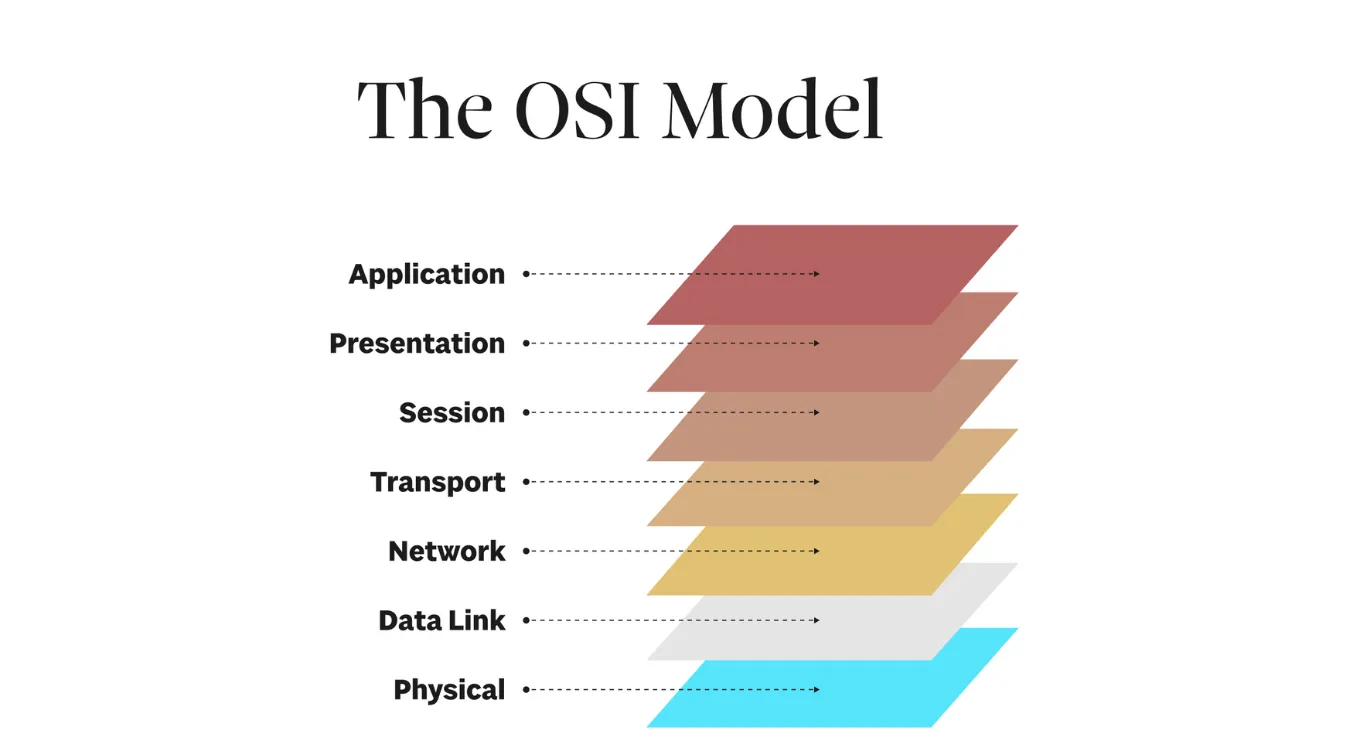
Place of the Data Link Layer in the OSI Stack
The data link layer sits directly above the physical layer and below the network layer.
The physical layer moves raw bits; the data link layer turns those bits into frames between neighbors.
The network layer (IP) then chains many of these local links into an end-to-end path.
Because each layer has a clear responsibility, designers can swap hardware or protocols without rewriting every part of the stack.
Switches, network interface cards, and wireless adapters all focus heavily on data link tasks.
Frames, MAC Addresses, and Local Delivery
At OSI layer 2, data travels as frames rather than packets.
Each frame carries a header, payload, and trailer, usually including:
Source MAC address
Destination MAC address
EtherType or protocol identifier
Optional VLAN tags
Error-checking field (for example, FCS)
Network interface cards create and parse frames.
Switches read MAC addresses, learn which ports host which devices, and forward frames accordingly.
Consequently, the local segment behaves like a shared but organized hallway instead of a random crowd.
Reliability and Access Control on the Link
The medium that carries frames can suffer from interference, collisions, and drops.
Therefore, the data link layer adds mechanisms that improve reliability and fairness.
Common functions include:
Error detection with checksums or frame check sequences
Optional retransmission on specific technologies
Flow control to avoid overrunning slower peers
Media access control (MAC) methods like CSMA/CD or CSMA/CA
Modern switched Ethernet reduces collisions, while Wi-Fi relies on careful contention rules.
These techniques keep local delivery efficient even when many devices compete for the same medium.
Variants and Sublayers: Ethernet, Wi-Fi, and More
The OSI model defines roles, not specific protocols.
In practice, different technologies implement layer 2 with their own frame formats and rules.
Typical examples:
Ethernet (IEEE 802.3): dominant wired LAN technology
Wi-Fi (IEEE 802.11): wireless LAN with its own management and control frames
PPP and HDLC: point-to-point links for serial and WAN connections
Additionally, IEEE 802.2 divides the layer into two sublayers:
Logical Link Control (LLC): identifies the upper protocol and manages multiplexing
Media Access Control (MAC): handles addressing and access to the physical medium
This split keeps some logic reusable across many link types.
Why the Data Link Layer Matters for Data Transfers
File copies, backup jobs, and remote recovery traffic eventually ride on layer 2 frames.
Even high-level storage protocols still rely on reliable local delivery between nodes.
When switches, NIC drivers, or Wi-Fi links misbehave, you see timeouts, stalls, and corrupted transfers.
In serious cases, a bad link contributes to file system damage or interrupted recovery operations.
By monitoring errors and link quality at layer 2, administrators protect the higher-value work above.
Tools such as Amagicsoft Data Recovery then operate over healthier paths when they move large volumes of recovered data back to servers or workstations.
Supports Windows 7/8/10/11 and Windows Server.
Supports Windows 7/8/10/11 and Windows Server
FAQ
What does a data link do?
What is an example of a data link?
What are the three main functions of the data link layer?
Why is the data link layer needed?
Is DLC the same as OBD?
What is the purpose of data linking?
What are the two types of data link layer?
What are layer 7 devices?
Is Bluetooth a data link layer?
Eddie is an IT specialist with over 10 years of experience working at several well-known companies in the computer industry. He brings deep technical knowledge and practical problem-solving skills to every project.