Environment Variable

Table of Contents
Why Environment Variables Matter to Recovery Work
A data recovery tool runs, but it cannot find a command, cannot write logs, or saves reports to an unexpected folder.
In many cases, the root cause is not the program itself but an environment variable that points to the wrong place.
Environment variables quietly influence how the operating system and tools behave.
They define paths, language settings, temp locations, and more.
If you understand how they work, you configure a safer and more predictable environment for tools like Amagicsoft Data Recovery.
What an Environment Variable Actually Is
An environment variable is a name–value pair that a process reads at runtime.
The operating system and applications rely on these pairs to decide where to find files, where to write temporary data, and how to format output.
Examples:
PATHcontrols which folders the system searches for executable files.TEMPandTMPdefine locations for temporary files.SYSTEMROOTpoints to the Windows directory.
When you launch a program, it inherits a snapshot of the current environment from its parent process.
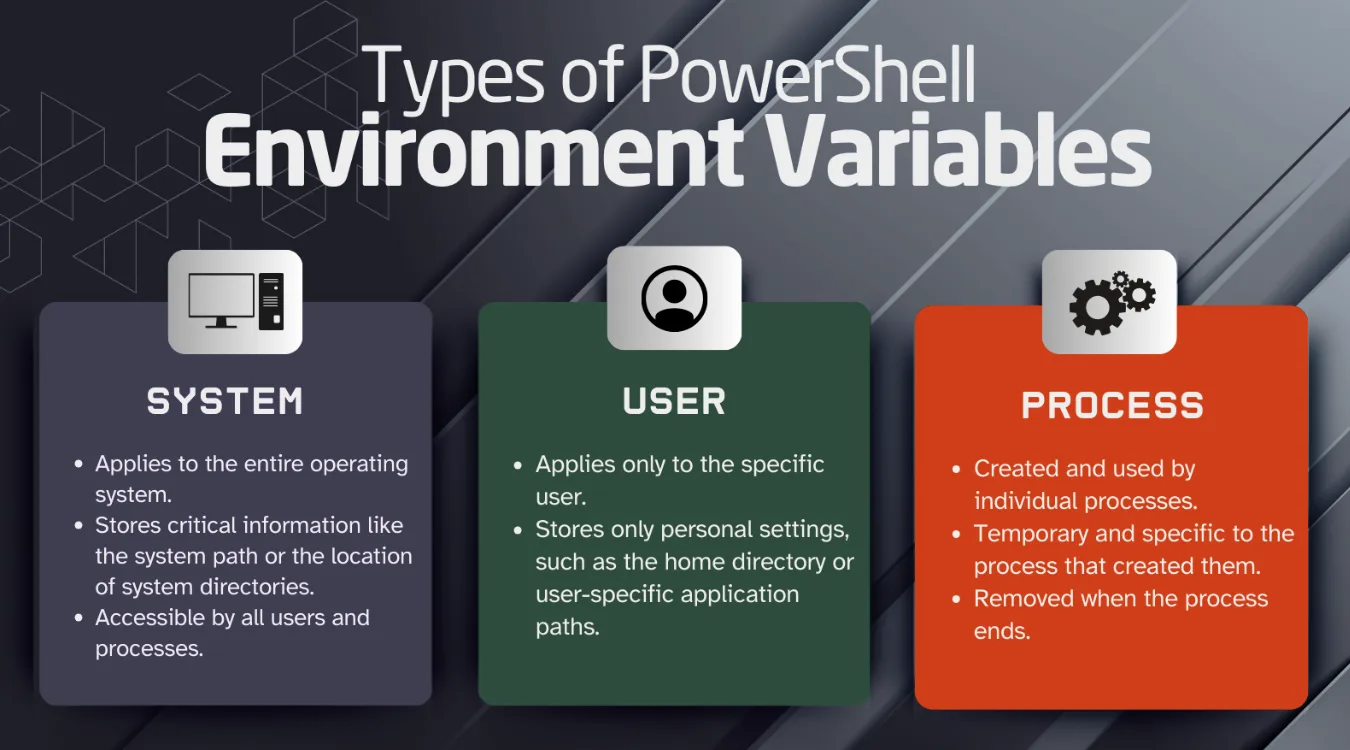
Scope of Environment Variables in Windows
Windows organizes environment variables into three main scopes:
System variables: Apply to every user. They define key locations like
PATH,ProgramData, and core OS directories.User variables: Apply only to the signed-in user. They control values like
USERPROFILEand user-specific paths.Process variables: Exist only inside one running process and its children. You can set them temporarily in Command Prompt or PowerShell.
Data recovery tools often rely on both system and user variables to locate profiles, desktop paths, and default save locations.
Key Environment Variables That Affect Recovery Tools
The following variables influence how utilities behave, especially when you handle damaged or external drives.
| Variable | Typical Purpose | Impact on Recovery Tools |
|---|---|---|
PATH | Search path for executables | Controls whether command-line tools launch successfully |
TEMP | Folder for temporary files | Affects where scans write caches and temporary data |
TMP | Alternative temp folder | Similar to TEMP; some tools prefer one or the other |
SYSTEMROOT | Windows system directory | Helps tools locate system files and libraries |
USERPROFILE | Current user profile folder | Defines default save paths and log locations |
HOMEDRIVE / HOMEPATH | Home drive and path | Influence scripts and batch jobs |
ProgramData | Shared application data folder | Central location for configuration and shared logs |
If TEMP points to a failing drive, a recovery scan may slow down or fail.
If PATH lacks required folders, certain helper tools never start.
Before a complex recovery, you should confirm that these values point to healthy, accessible locations.
How Recovery and Forensic Tools Use Environment Variables
Data recovery and forensic applications do more than scan sectors.
They also log events, store configuration, and call other utilities.
Typical uses include:
Locating executables: Command-line helpers depend on
PATHto run without a full path.Storing temporary data: Deep scans write large temporary structures to
TEMPorTMP.Writing logs: Many applications place log files under
ProgramDataor a path based onUSERPROFILE.Respecting locale: Variables related to language and code page can affect how file names and timestamps appear.
When you run Amagicsoft Data Recovery, a clean environment ensures that:
Logs and temp files land on a healthy system drive, not on the failing disk.
The tool has access to needed system components.
Paths with non-ASCII characters resolve correctly.
You reduce surprises and improve the repeatability of scan results.
Supports Windows 7/8/10/11 and Windows Server
Viewing and Setting Environment Variables in Windows
You can inspect and change environment variables in several ways.
Each method suits a different situation.
Using the Windows GUI
To edit environment variables through the graphical interface:
Right-click This PC and choose Properties.
Select Advanced system settings.
Click Environment Variables.
Review User variables and System variables.
Select a variable such as
TEMPorPATH, then click Edit to change its value.
This method works well for permanent changes that apply to future sessions.
Using Command Prompt (cmd.exe)
In Command Prompt, you manage environment variables per session.
View a single variable:
echo %TEMP%Set a variable for the current session:
set MYVAR=TestValueList all variables:
set
Changes you make with set in a Command Prompt window remain active only until you close that window.
This behavior is useful when you run a one-time recovery session and want to redirect temporary files away from a failing disk.
Using PowerShell
PowerShell exposes environment variables through the Env: drive.
View a variable:

Set a variable for the current session:

List all variables:

You can also use [System.Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable() to write persistent user or system variables, but session-only changes are safer when you experiment.
Troubleshooting Common Environment Variable Issues
Several recurring problems affect tools and recovery work.
Broken or Overwritten PATH
A damaged PATH may prevent key tools from starting.
You can:
Use
echo %PATH%or$Env:PATHto view the current content.Compare it with a known good configuration.
Add missing folders such as
C:\Windows\System32or the directory that contains your recovery utilities.
Always back up the existing value before you modify it.
TEMP on a Failing or Full Drive
If TEMP points to a failing disk or a full partition, scans slow down or crash.
You should:
Create a dedicated temp folder on a healthy drive, for example
D:\TempRecovery.Point
TEMPandTMPto that folder for the current session.Launch Amagicsoft Data Recovery from the same session and start the scan.
This approach keeps the failing disk in read-only use and protects temporary indexes and logs.
Incorrect Profiles and Permissions
When you run tools under different accounts, variables like USERPROFILE change.
You may think a program writes logs to one folder while it writes to another account’s directory.
To avoid confusion:
Confirm which user runs the recovery tool.
Check
whoamiand the currentUSERPROFILEvalue.Save recovered files to a clearly chosen path on a healthy drive.
Supports Windows 7/8/10/11 and Windows Server
Best Practices for Environment Variables During Recovery
You improve stability and safety with a few simple rules:
Keep a backup of critical variables such as
PATH,TEMP, andSYSTEMROOT.Use temporary, session-based changes for experiments or one-time recovery jobs.
Point
TEMPandTMPto a healthy, spacious drive during large scans.Avoid storing recovery logs or recovered files on a disk that shows errors.
Document any persistent changes you make so you can reverse them later.
When you prepare a clean environment and then run Amagicsoft Data Recovery, you give the tool consistent paths, enough temporary space, and a clear separation between damaged and healthy volumes.
Supports Windows 7/8/10/11 and Windows Server.
FAQ
What is meant by environment variable?
What are examples of environmental variables?
Where are environment variables?
What is the environment variable in Windows?
How do you set an environment variable?
How to check if an environment variable is set in Windows?
How do I get the list of all environment variables?
Eddie is an IT specialist with over 10 years of experience working at several well-known companies in the computer industry. He brings deep technical knowledge and practical problem-solving skills to every project.