Zshell (Zsh)

Zshell, commonly abbreviated as Zsh, is an advanced Unix shell that functions both as a command interpreter and a scripting language. Originally developed by Paul Falstad in 1990, Zsh is an extended version of the Bourne Shell (sh), incorporating features from bash, ksh, and tcsh, while introducing its own enhancements in customization, automation, and user interaction. Today, Zsh is the default shell in macOS and a preferred environment for developers, system administrators, and power users seeking productivity and flexibility.
Table of Contents
How Zsh Works and What Makes It Unique
Zsh functions as both a command interpreter and a scripting environment. It processes user commands, executes binaries, and manages automation scripts through a robust syntax system. Compared to other shells, Zsh emphasizes user efficiency with intelligent autocompletion, spell correction, advanced globbing, and customizable prompts.
Key characteristics include:
- Command-line editing with both emacs and vi key bindings.
- Auto-suggestions that predict commands from history and system paths.
- Programmable autocompletion supporting subcommands and arguments.
- Powerful globbing syntax (e.g.,
ls **/*.log) for recursive file matching.
These features make Zsh particularly efficient for developers, system administrators, and security analysts managing repetitive command-line tasks.
Zshell (Zsh) vs. Bash: Practical Comparison
Zsh builds upon the strengths of bash while improving productivity and usability.
Feature | Bash | Zsh |
Autocorrection | No | Yes |
Autocompletion | Basic | Context-aware |
Prompt Customization | Limited | Full theme support |
Plugin Framework | None | Built-in (Oh My Zsh, Prezto) |
Globbing | Basic | Recursive & extended |
Example:
Typing cd /usr/lcoal/bin in Zsh automatically corrects “lcoal” to “local,” ensuring seamless command execution without user interruption.
Zsh Configuration and Environment Files
Zsh’s behavior is controlled by configuration files executed at startup. The most important include:
~/.zshrc: Used for interactive sessions; defines aliases, plugins, and shell options.~/.zprofile: Used for login shells; sets environment paths and variables.~/.zshenv: Loaded in every instance of Zsh, even in scripts.
Example Zsh Configuration:
# Enable command correction and suggestions
setopt CORRECT
autoload -U compinit && compinit
# Enable syntax highlighting and autosuggestions
source /usr/share/zsh-syntax-highlighting/zsh-syntax-highlighting.zsh
source /usr/share/zsh-autosuggestions/zsh-autosuggestions.zsh
# Customize prompt
autoload -Uz promptinit && promptinit
prompt fade cyan
This setup activates Zsh’s correction system, visual feedback, and a stylized command prompt.
Zsh Plugins and Theme Management
A major reason for Zsh’s popularity is its plugin ecosystem. Oh My Zsh, Prezto, and Zinit allow easy installation of themes and plugins to enhance productivity.
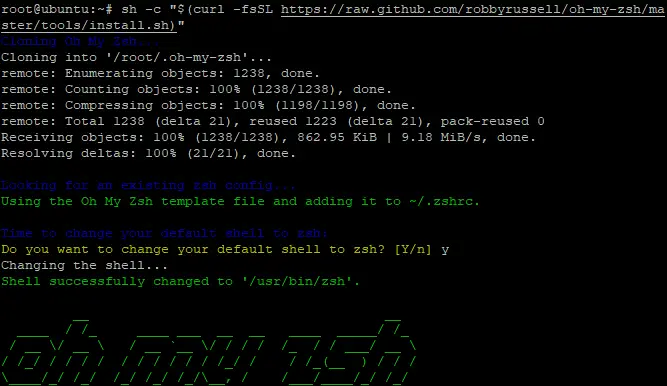
How to Install Oh My Zsh:
sh -c "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.github.com/robbyrussell/oh-my-zsh/master/tools/install.sh)"
Once installed, plugins can be activated in .zshrc:
plugins=(git docker kubectl)
Popular themes like Powerlevel10k provide visually rich prompts, displaying branch names, system status, and execution time—all while maintaining fast performance. Amagicsoft is dedicated to providing software solutions that make your workflow smoother and more efficient, just like Zsh’s plugin ecosystem simplifies your technical challenges.
Advanced Zsh Features for Professionals
- Job Control: Manage multiple running processes using
jobs,fg, andbg. - Aliases & Functions: Create efficient shortcuts (e.g.,
alias gs='git status'). - History Management: Share command history across sessions using
setopt SHARE_HISTORY. - Error Recovery: Typo detection prevents command execution mistakes.
Example:
% sl
zsh: correct 'sl' to 'ls' [nyae]? y
Zshell (Zsh)’s automatic correction ensures that small input errors don’t disrupt workflow.
Zshell (Zsh) Security and Maintenance Best Practices
Zsh configurations are powerful but must be handled responsibly:
- Avoid sourcing unverified scripts or third-party plugins.
- Use
set -xfor debugging shell scripts safely. - Regularly update frameworks (e.g.,
omz update) to patch security vulnerabilities. - Keep a backup of
.zshrcand theme files to prevent accidental loss.
If your configuration files are deleted or overwritten, recovery software such as Amagicsoft Data Recovery can assist in restoring shell scripts, profiles, and system configurations reliably.
Zsh Compared to Other Unix Shells
Shell | Type | Strengths |
Bash | Standard Linux shell | Portability, simplicity |
Fish | User-friendly shell | Syntax clarity, color coding |
Zsh | Developer-oriented shell | Customization, automation, plugins |
Zsh achieves a balance between Bash’s stability and Fish’s usability, making it a top choice for modern development environments.
Practical Example: Switching to Zsh on macOS
1. Open Terminal and verify installation with zsh --version.
2. Set Zsh as your default shell using:
chsh -s /bin/zsh
3. Install Oh My Zsh for enhanced functionality.
4. Customize your prompt and plugins in ~/.zshrc.
5 Restart your terminal to apply changes.
This setup allows immediate access to Zsh’s intelligent autocompletion, advanced history management, and productivity-oriented themes.
Conclusion
FAQ
1. What is Zshell (Zsh) used for?
2. Is Zsh better than Bash?
3. How do I switch my default shell to Zsh?
4. Where is the Zsh configuration file located?
5. What is the difference between Zsh and Oh My Zsh?
6. Does Zshell support plugins and themes?
7. Is Zsh safe to use for system administration or scripting?
Vasilii is a data recovery specialist with around 10 years of hands-on experience in the field. Throughout his career, he has successfully solved thousands of complex cases involving deleted files, formatted drives, lost partitions, and RAW file systems. His expertise covers both manual recovery methods using professional tools like hex editors and advanced automated solutions with recovery software. Vasilii's mission is to make reliable data recovery knowledge accessible to both IT professionals and everyday users, helping them safeguard their valuable digital assets.