What is FAT16 File System

FAT16 File System (File Allocation Table 16) is an early disk file system developed by Microsoft and widely used in DOS and early Windows operating systems. It represents one of the earliest structured approaches to managing files on block-based storage devices. Although largely obsolete today, FAT16 file system is still encountered in legacy systems, embedded devices, industrial equipment, and older removable media.
From a data recovery perspective, FAT16 is relatively simple compared to modern file systems like NTFS. This simplicity can be an advantage during recovery, as file structures are easier to interpret, but it also introduces significant limitations in capacity, reliability, and fault tolerance.
Table of Contents
How FAT16 File System Works
FAT16 organizes data using a centralized File Allocation Table (FAT) that tracks the status of each cluster on the disk. Each entry in the table is 16 bits wide, allowing a maximum of 65,536 addressable clusters.
Key structural components include:
- Boot Sector:
Contains essential file system parameters such as sector size, cluster size, and FAT location.
- File Allocation Table:
Acts as a linked list mapping clusters that belong to a file. Each entry points to the next cluster in the chain or marks the end of the file.
- Root Directory:
A fixed-size directory area that stores file metadata such as file name, size, timestamps, and starting cluster.
- Data Area:
The region where actual file content is stored.
Unlike NTFS, FAT16 does not use metadata journaling or advanced attributes. Its structure is flat, predictable, and straightforward.

FAT16 File System Capacity and Limitations
FAT16 file system was designed for small storage devices by modern standards. Its major limitations include:
- Maximum Volume Size: Typically limited to 2 GB
- Maximum File Size: Up to 2 GB
- Fixed Root Directory Size: Limited number of entries
- No Journaling: Increased risk of corruption after power loss
- No Permissions or Encryption: Minimal security controls
These constraints make FAT16 unsuitable for modern operating systems, but they remain acceptable in environments where simplicity and compatibility are required.
FAT16 vs FAT32
Feature | FAT16 | FAT32 |
Max volume size | ~2 GB | ~2 TB |
Journaling | No | No |
Security permissions | No | No |
Root directory | Fixed | Dynamic |
Recovery complexity | Low | Medium |
FAT16’s simplicity reduces overhead but sacrifices resilience and scalability.
FAT16 File System Data Deletion Behavior
When a file is deleted on a FAT16 volume:
- The directory entry’s first character is replaced with a deletion marker
- The cluster chain is marked as free in the FAT
- Actual file data remains on disk until overwritten
This behavior allows recovery tools to reconstruct deleted files by scanning directory entries, FAT remnants, and raw data clusters.
Common FAT16 Data Loss Scenarios
Because FAT16 file system lacks journaling and redundancy, it is vulnerable to several common failure modes:
- Improper device removal
- Power loss during write operations
- File system corruption
- Accidental deletion
- Logical formatting
- Boot sector damage
If a FAT16 volume becomes unreadable, the operating system may report it as unformatted or inaccessible. The good news is that data is often still present on disk even when directory entries are damaged. Professional tools like Magic Data Recovery can recover the data easily.
How to Recover Data From FAT16 Drives?
Magic Data Recovery is specifically optimized for legacy file systems like FAT16, it can rapidly scan FAT tables and root directories. Even when critical file system metadata is missing or damaged, Magic Data Recovery employs deep signature-based scanning to recover over 5,000 file types by recognizing their unique binary patterns—ensuring high recovery success rates from outdated or corrupted media. Here are the steps to recover the data:
1. Download and Install Magic Data Recovery.
You need to install the software to another drive in case the lost files get damaged.
Supports Windows 7/8/10/11 and Windows Server
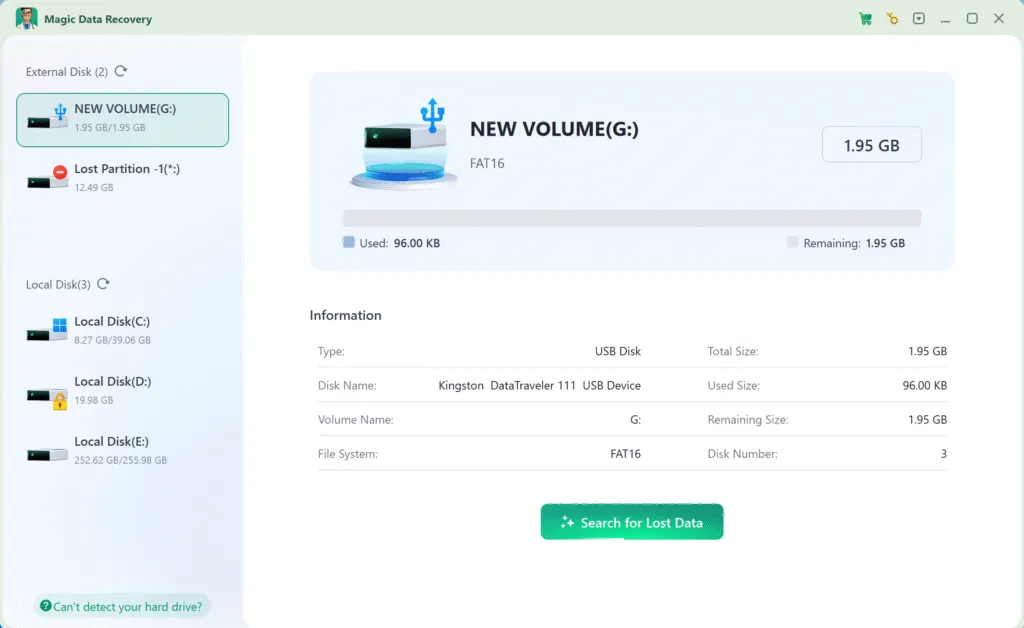
2. Select the FAT16 drive and start a scan.
When you run the software, it will list all the drives connected to the drive. Select the FAT16 drive and start a scan.
3. Wait till the scan complets.
It runs Advanced Scan automatically to find every possible file. The time for the scan mainly depends on the capacity and performance of the drive.
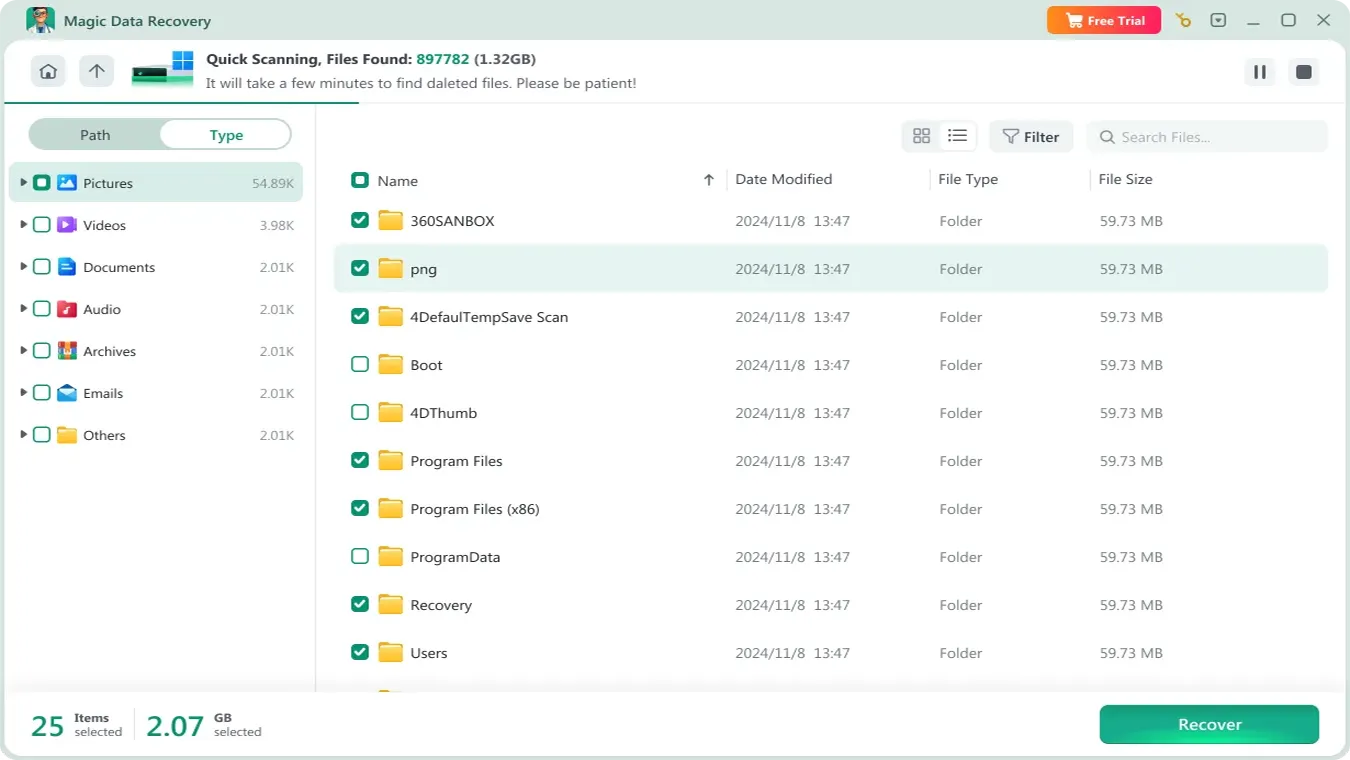
4. Preview files.
When the scan completes, it will list all the files it can find. You can use the Preview feature to check the file contents and confirm whether they are the files you are looking for.

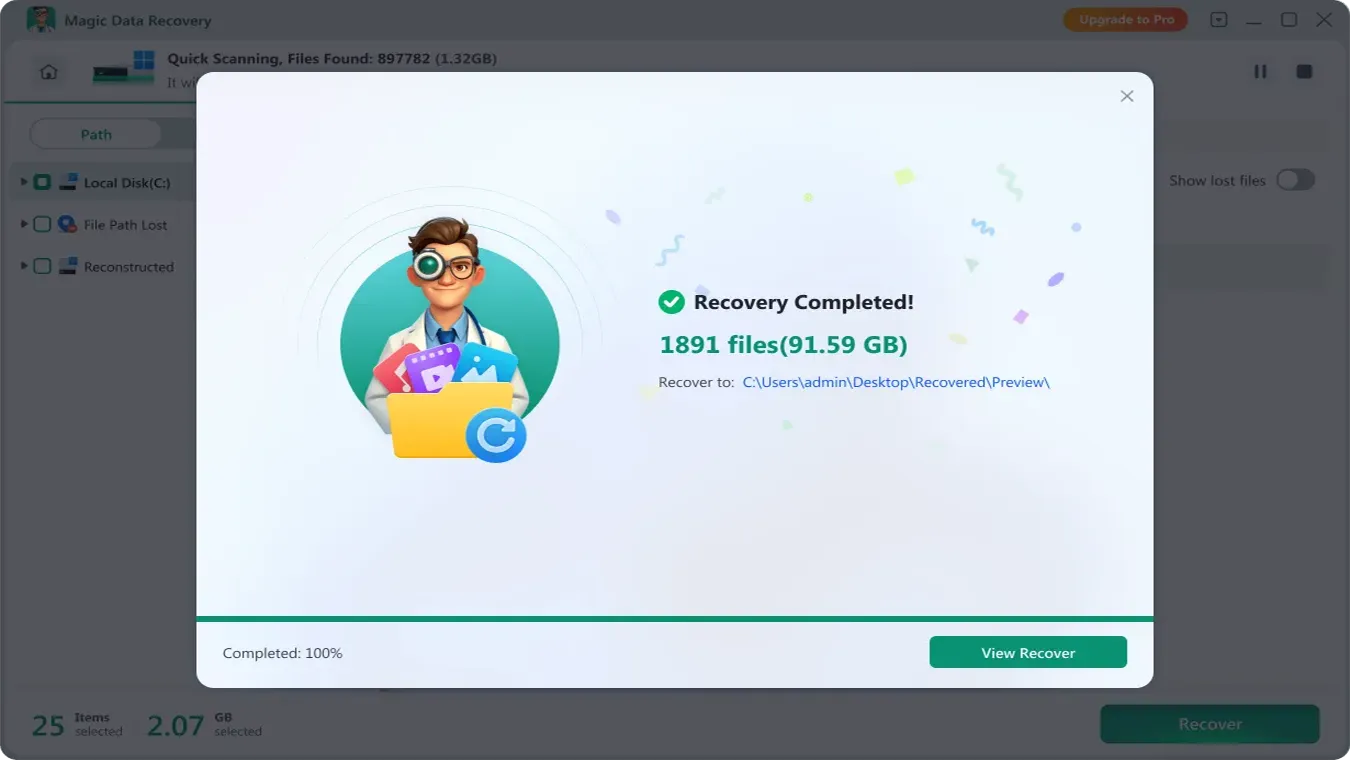
5. Recover data.
Select the files you need and recover them to another drive. Do Not recover the data to the original FAT16 drive directly in case the files get damaged.
Conclusion
Supports Windows 7/8/10/11 and Windows Server
FAT16 File System FAQs
1.Is FAT16 a file system?
2.Is FAT32 better than FAT16?
3.Is NTFS the same as FAT16?
4.Can Windows 10 format FAT16?
5.What is better, FAT or NTFS?
6.Do people still use FAT?
Vasilii is a data recovery specialist with around 10 years of hands-on experience in the field. Throughout his career, he has successfully solved thousands of complex cases involving deleted files, formatted drives, lost partitions, and RAW file systems. His expertise covers both manual recovery methods using professional tools like hex editors and advanced automated solutions with recovery software. Vasilii's mission is to make reliable data recovery knowledge accessible to both IT professionals and everyday users, helping them safeguard their valuable digital assets.



