What is FAT32 File System

FAT32 File System (File Allocation Table 32) is a disk file system introduced by Microsoft in 1996 as an extension of the original FAT architecture. It uses a 32-bit file allocation table to manage data storage, allowing more efficient space usage than FAT16 while maintaining broad compatibility across operating systems, devices, and embedded systems. FAT32 file system is commonly used on USB flash drives, SD cards, and external storage devices where cross-platform support is essential.
Table of Contents
How FAT32 File System Works
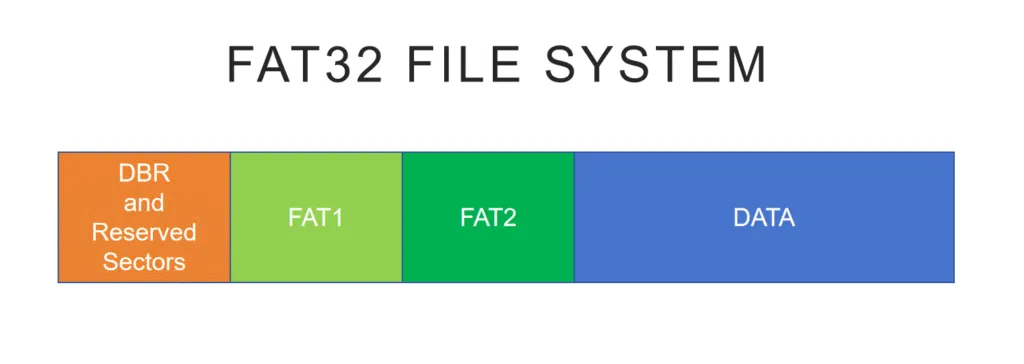
Compared to FAT16, FAT32 supports smaller cluster sizes on large volumes, reducing wasted space. However, despite its name, FAT32 does not allow an individual file larger than 4 GB, a design limitation defined by its 32-bit addressing structure.
Why FAT32 File System Is Still Widely Used
Although newer file systems like NTFS and exFAT exist, FAT32 file system remains relevant for several practical reasons:
- Universal compatibility: Supported by Windows, macOS, Linux, game consoles, smart TVs, cameras, and firmware-level systems.
- Low overhead: Simple structure makes it lightweight and fast for removable media.
- Boot and firmware support: Many BIOS, UEFI, and embedded devices require FAT32-formatted media.
For these reasons, FAT32 is often the default or required format for USB drives used in cross-device environments.
FAT32 vs NTFS
Feature | FAT32 | NTFS |
Max file size | 4 GB | 16 TB (theoretical) |
Max volume size | 2 TB (Windows tools limit to 32 GB formatting) | 256 TB+ |
Journaling | No | Yes |
Permissions & encryption | No | Yes |
Cross-platform support | Excellent | Limited outside Windows |
FAT32 prioritizes compatibility, while NTFS focuses on reliability, security, and scalability.
Common FAT32 File System Limitations
While reliable for removable storage, FAT32 file system has notable drawbacks:
- No file-level security: No permissions, encryption, or access control.
- No journaling: Higher risk of corruption after unsafe removal.
- File size limit: Cannot store files larger than 4 GB.
- Fragmentation: Performance may degrade over time on heavily used volumes.
These constraints make FAT32 unsuitable for modern operating systems or large-scale data storage.
How to Format a USB Drive to FAT32 File System
1. Insert the USB drive.
2. Open Disk Management.
3. Right-click the USB partition and select Format.
4. Choose FAT32 as the file system.
5. Confirm the operation.
Note: Windows’ built-in tools may restrict FAT32 formatting to drives ≤32 GB. Third-party utilities or command-line tools can bypass this limitation.
Data Safety Considerations
If a FAT32 volume becomes corrupted or accidentally formatted, the file allocation table may be damaged while the data itself remains intact. In such cases, a read-only recovery approach is critical to prevent further data loss. Professional tools like Magic Data Recovery can scan FAT32 volumes safely and reconstruct files by analyzing residual cluster chains without modifying the original disk. Here are the steps to recover the data:
1. Download & Install the Software
Install Magic Data Recovery on a different drive to prevent overwriting lost files. Do not install it on the FAT32 drive you’re trying to recover data from.
Supports Windows 7/8/10/11 and Windows Server
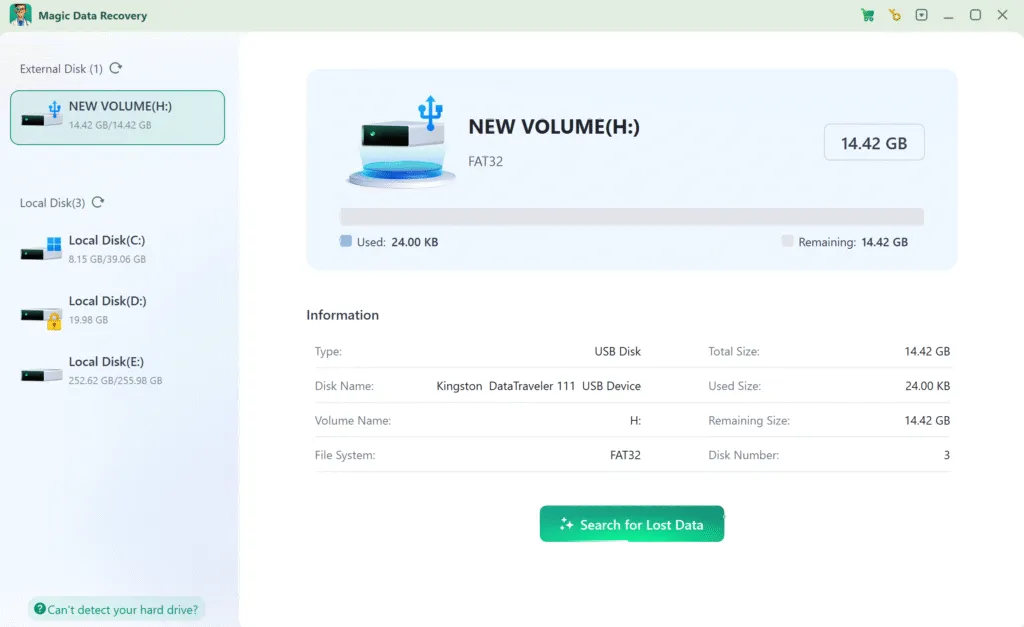
2.Select the FAT32 Drive & Start Scanning
Launch the software. It will automatically detect all connected drives.
→ Select the FAT32 drive containing the lost files.
→ Click “Search” to begin the recovery process.
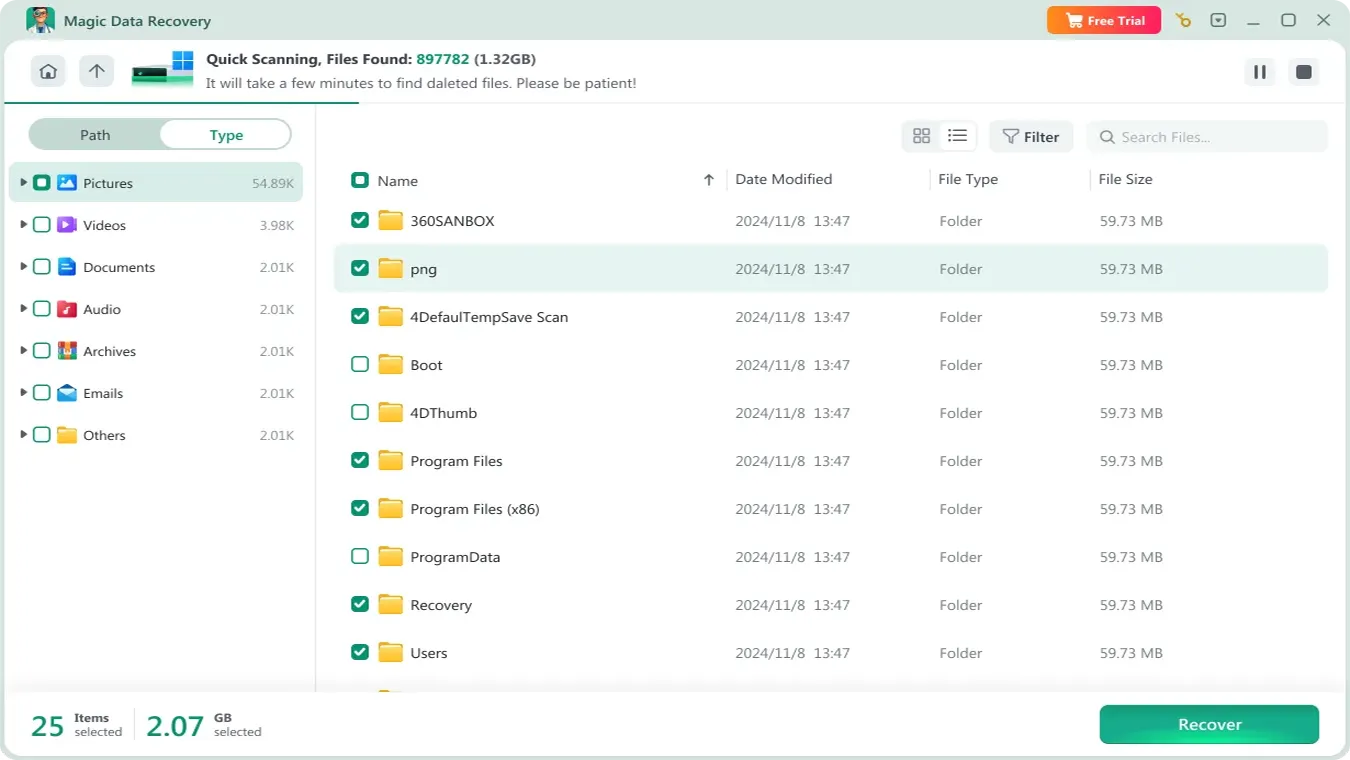
3. Wait for the Scan to Complete
The software performs an Advanced Scan to locate all recoverable files. Scan time mainly depends on the drive’s capacity and performance.
4. Preview Files Before Recovery
Once scanning finishes, all found files appear in the results list. Use the “Preview” feature to open files (e.g., photos, documents) and verify they match your lost data.

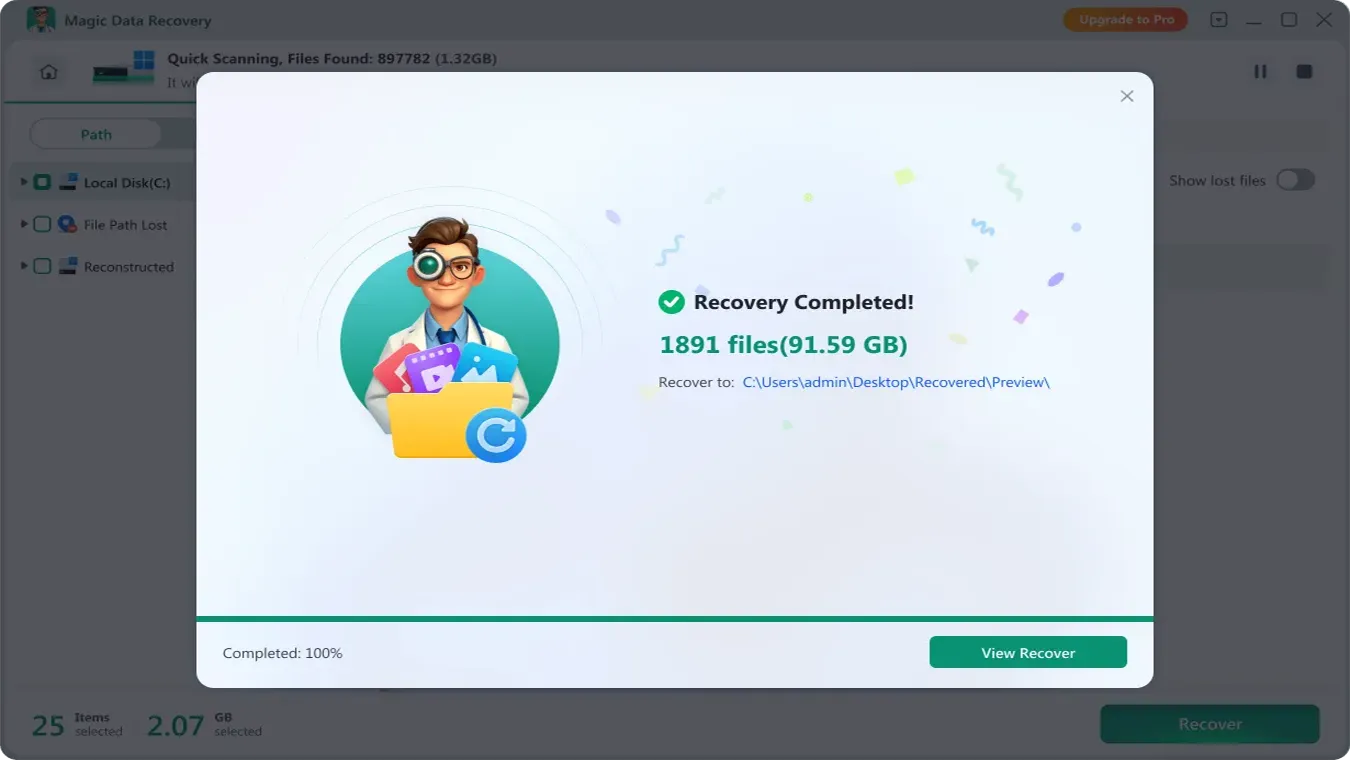
5.Recover Data Safely
Select the files you need and click “Recover” button to choose a different drive (e.g., an external USB or secondary internal drive).
⚠️ ABSOLUTELY DO NOT recover files to the original FAT32 drive—this risks overwriting and permanent data loss.
Conclusion
Supports Windows 7/8/10/11 and Windows Server
FAT32 File System FAQ
1.What does FAT32 mean for USB?
2.Which is better, FAT32 or NTFS?
3.Are all 32GB SD cards FAT32?
4.Is FAT32 still in use?
5.Do all USB drives support FAT32?
6.How do I put my USB in FAT32?
7.What are the downsides of FAT32?
8.Can I convert FAT32 to NTFS?
Vasilii is a data recovery specialist with around 10 years of hands-on experience in the field. Throughout his career, he has successfully solved thousands of complex cases involving deleted files, formatted drives, lost partitions, and RAW file systems. His expertise covers both manual recovery methods using professional tools like hex editors and advanced automated solutions with recovery software. Vasilii's mission is to make reliable data recovery knowledge accessible to both IT professionals and everyday users, helping them safeguard their valuable digital assets.



