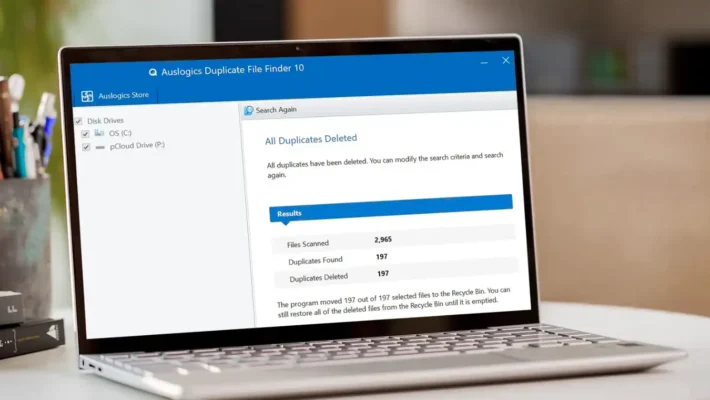
資料可視化

目錄
Turning Raw Data Into Visual Insight
Spreadsheets full of numbers rarely tell a clear story at a glance.
Teams want to see trends, exceptions, and relationships without reading thousands of rows.
Data visualization solves that need.
It encodes values as shapes, positions, lengths, and colors so patterns become obvious, and important anomalies stand out immediately.
Building Blocks of a Useful Visualization
Effective visuals combine three elements: data, visual encodings, and context.
Typical encodings include:
Position on an axis (strong for comparing values)
Length and area (bars and columns)
Color hue or intensity (categories or density)
Shape and size (groups or emphasis)
Context comes from titles, labels, units, and notes.
Clear context lets viewers understand exactly what each mark on the chart represents.
Data Visualization in an Analytical Workflow
Visualization does not stand alone.
It fits into a broader analysis pipeline that turns raw sources into decisions.
A common workflow looks like this:
Collect and profile data from databases, logs, files, or APIs.
Clean and transform fields, handle missing values, and create calculated metrics.
Choose visual forms that match the questions and data types.
Iterate with stakeholders, refining focus, filters, and annotations.
Publish or embed dashboards and reports where people work every day.
Each step affects the clarity and reliability of the final charts.
Matching Visual Forms to Questions
Different questions call for different chart types.
Choosing an appropriate form matters as much as the data itself.
Common families:
比較: bar charts, column charts, grouped bars
Trend: line charts, area charts, sparklines
Distribution: histograms, box plots, violin plots
Relationship: scatter plots, bubble charts, correlation matrices
Composition: stacked bars, 100% stacked bars, waterfall charts
Maps, heatmaps, and network diagrams extend these ideas into space and relationships when location or connectivity matters.
Practical Design Guidelines for Clear Charts
Clean design helps viewers understand visuals quickly.
A few disciplined habits make a big difference.
建議的做法:
Use simple, legible fonts and avoid decorative effects.
Limit color palettes; reserve bright colors for emphasis.
Start axes at zero when you compare magnitudes with bars.
Avoid 3D effects that distort perception.
Label directly where possible instead of relying only on legends.
Every extra element should justify its presence by adding clarity, not decoration.
Visualizing Storage and Recovery Metrics
在 資料復原 and system maintenance, visualization helps teams monitor risks and results.
Instead of scanning log files, they see patterns directly.
Examples that benefit from charts:
Counts of failed versus successful recovery jobs by day
Distribution of file types recovered from damaged volumes
SMART attributes from disks over time (temperature, reallocated sectors)
Trend lines of remaining free space on backup targets
By exporting logs from tools such as Amagicsoft 資料復原 into Excel or BI platforms, technicians can build dashboards that reveal early warnings before data loss grows severe.
Simple Visualization Workflow With Common Tools
Many teams start with tools they already know: spreadsheets and basic BI.
A practical approach:
Export recovery logs, drive inventories, or performance metrics to CSV.
Load the file into Excel, Power BI, or another visualization tool.
Create pivot tables that summarize recovery counts, sizes, or error types.
Turn those summaries into charts or small dashboards.
Share updated files or publish reports on an internal portal.
支援 Windows 7/8/10/11 和 Windows Server。.
總結
Data visualization turns abstract tables into interpretable scenes.
Good charts highlight trends, clusters, and anomalies so teams react quickly and confidently.
In technical domains such as storage management and 資料復原, visuals give clear evidence of risk and progress.
Combined with reliable tools like Amagicsoft 資料復原, they help organizations move from raw logs to informed, traceable decisions.
支援 Windows 7/8/10/11 和 Windows Server
常見問題
What is meant by data visualizatio
What do you mean by data visualizer?
What are the 5 steps in data visualization?
What are the four types of data visualization?
What are the 5 C's of data visualization?
Can ChatGPT do data visualization?
What are the 3 C's of data visualization?
Is SQL for data visualization?
Is data visualization a hard skill?
Eddie 是一位 IT 專家,在電腦行業的幾家知名公司擁有超過 10 年的工作經驗。他為每個專案帶來深厚的技術知識和實際的問題解決技巧。.