Validierung von Daten
Inhaltsübersicht
Data Quality Problems Start at the Input
Many systems fail long before disks or applications break.
They fail quietly when a form accepts the wrong date, a script writes an invalid ID, or a backup job logs “success” with incomplete values.
Those small errors travel into reports, dashboards, and even recovery workflows.
Data validation stops that drift by checking each value against clear technical rules before it enters your core datasets.
Core Idea Behind Data Validation
Data validation means checking incoming data for accuracy, completeness, and consistency before storage or processing.
You can run these checks at the UI, the API, the ETL pipeline, or directly in the database.
Typical goals:
Reject clearly invalid values
Flag suspicious or incomplete records
Normalize formats into predictable patterns
Protect downstream systems from bad input
Instead of trusting every value, your systems challenge each one, then accept, correct, or reject it in a controlled way.
Types of Validation Rules and Their Role
You rarely rely on a single rule.
Most implementations combine several validation types to cover different risks.
| Validation Type | Schwerpunkt | Simple Example |
|---|---|---|
| Format / Syntax | Structure of a value | Email must contain “@” and domain |
| Range / Limit | Numeric or date boundaries | Age between 0 and 120 |
| Referential / Lookup | Relationship to other data | Order uses an existing customer ID |
| Business Logic | Domain-specific conditions | End date occurs after start date |
Together, these rules form a safety net around critical fields such as IDs, timestamps, and amounts.
Where Validation Lives: UI, Services, and Storage
Robust systems do not rely on a single validation layer.
They combine checks at multiple points in the flow.
On the User Interface
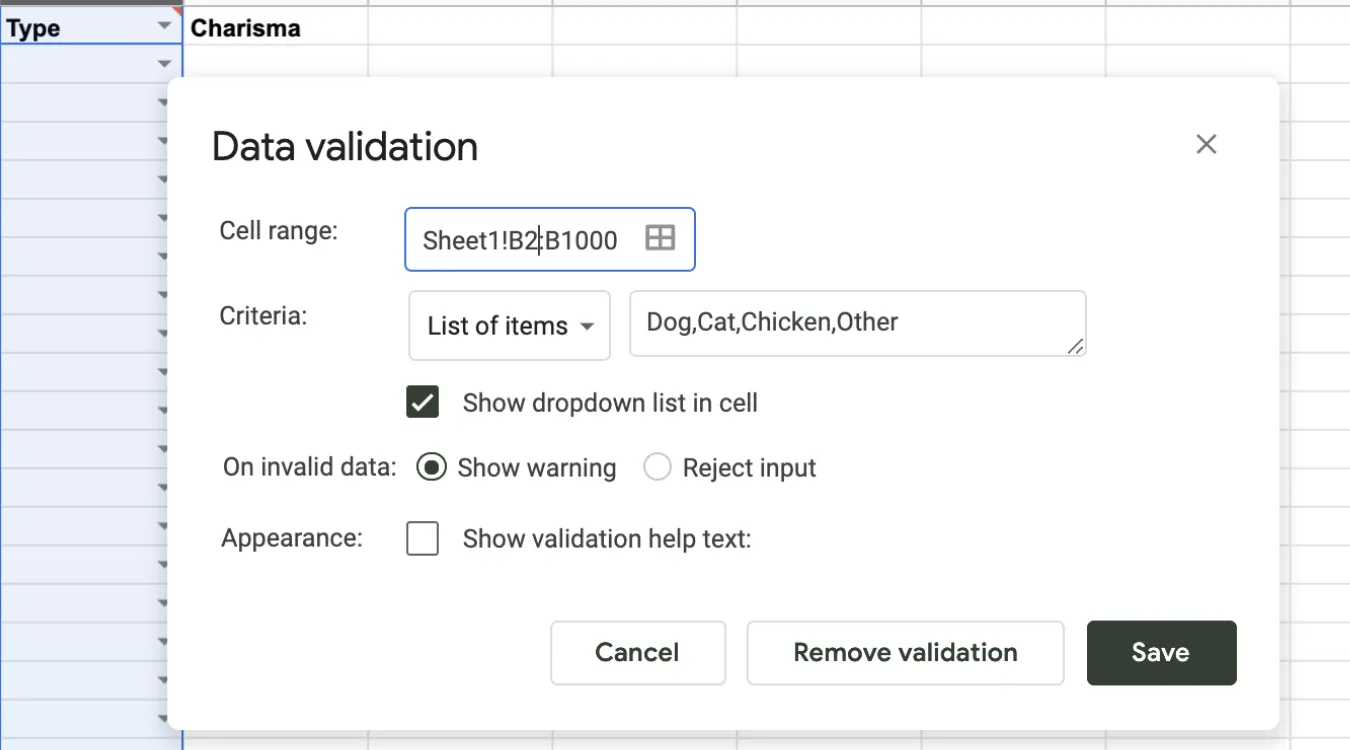
Forms enforce required fields and formats.
Dropdown lists limit choices to valid items.
Real-time hints steer users toward valid input.
You reduce simple mistakes early, but you still treat the UI as untrusted because automation and scripts can bypass it.
In APIs and Services
REST or RPC endpoints validate payload structure and types.
Services apply business rules and permissions.
Central logic keeps behavior consistent across clients.
This layer protects internal data even when new front ends appear.
Inside Databases and ETL Jobs
Database constraints, triggers, and check clauses enforce strict rules.
ETL processes validate imported files and log rejected rows.
Batch jobs reconcile aggregates to catch missing or duplicated data.
This deeper layer guards long-term storage, where corrupted values matter most.
Implementing Validation in SQL and Storage Systems
Relational databases provide strong tools for validation close to the data.
You can combine them with application-level checks for better coverage.
Common mechanisms:
Data types: use the most specific type (DATE, INT, DECIMAL) instead of generic strings.
CHECK constraints: enforce ranges or patterns on columns.
FOREIGN KEY constraints: guarantee valid relationships between tables.
UNIQUE constraints: prevent duplicate keys or identifiers.
For log and backup catalog tables that support tools such as Amagicsoft Datenrettung, these constraints ensure that job records, paths, and timestamps remain trustworthy during audits or incident analysis.
Unterstützt Windows 7/8/10/11 und Windows Server
Practical Steps for a Data Validation Workflow
A systematic approach keeps validation maintainable and auditable.
Define the contract
List required fields, allowed ranges, formats, and relationships for each dataset.Map rules to layers
Decide which checks run in the UI, which live in the API, and which belong in the database.Implement and centralize business rules
Use reusable functions, shared libraries, or stored procedures so multiple services follow identical logic.Log failures and anomalies
Log every rejection with reasons. Over time, patterns highlight weak inputs or misunderstood rules.Test regularly
Create test cases with valid, borderline, and invalid values to confirm that rules behave as intended.
Data Validation in Backup and Recovery Contexts
For backup, archive, and Datenwiederherstellung workflows, validation supports both safety and traceability.
Beispiele:
Backup jobs validate source paths and schedules before running.
Recovery tools validate destination volumes and free space before restoring.
Catalogs validate job statuses and sizes so reports match reality.
Amagicsoft Datenrettung, for instance, benefits from accurate job metadata.
When logs and paths pass validation, technicians can filter and interpret scan results correctly and reduce the chance of restoring to the wrong location.
Unterstützt Windows 7/8/10/11 und Windows Server.
Unterstützt Windows 7/8/10/11 und Windows Server
Summary for Practitioners
Data validation converts vague assumptions about “clean data” into explicit, testable rules.
Those rules shield analytics, compliance work, and recovery operations from silent corruption.
By distributing checks across UI, services, and storage, and by logging every failure, you gain both higher quality and better forensic visibility.
The result: fewer surprises when you need reliable data the most.
Häufig gestellte Fragen
What do you mean by data validation?
What are the four types of data validation?
What does validation data do?
What is data validation in SQL?
In SQL, data validation relies on data types, constraints, and relationships defined inside the schema. You enforce ranges with CHECK constraints, uniqueness with UNIQUE keys, and relationships with FOREIGN KEY constraints. These rules stop invalid rows at the database boundary and protect downstream queries, reports, and integrations from corrupt values.
What are the 4 levels of validation?
How do you validate data?
Why is data validation needed?
What is an example of validation?
What are the three steps of data validation?
Eddie ist ein IT-Spezialist mit mehr als 10 Jahren Erfahrung, die er bei mehreren bekannten Unternehmen der Computerbranche gesammelt hat. Er bringt tiefgreifende technische Kenntnisse und praktische Problemlösungsfähigkeiten in jedes Projekt ein.