Che cos'è il file system NTFS

NTFS (New Technology File System) is a proprietary journaling file system developed by Microsoft and used as the default file system for modern Windows operating systems, including Windows 10 and Windows 11. It was designed to overcome the limitations of earlier file systems such as FAT32 by providing improved reliability, security, scalability, and performance for modern storage environments.
From a data recovery and digital forensics perspective, NTFS is considered a robust and information-rich file system. Its internal metadata structures preserve extensive details about files, permissions, and changes, which often makes professional recovery possible even after cancellazione accidentale o corruzione del file system.
Indice dei contenuti
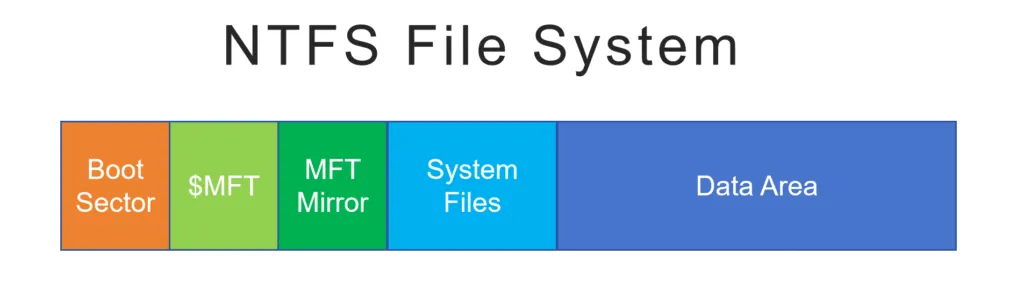
NTFS File System Structure
NTFS is a robust and highly structured file system designed for the Windows NT family of operating systems. Its overall structure can be divided into several key regions that ensure data organization, security, and integrity:
1. Boot Sector (Partition Boot Sector)
The NTFS volume begins with the Boot Sector (also known as the Partition Boot Sector, or PBS). This critical sector is located at the very start of the volume.
- It contains the Bootstrap Code (the code needed to load the operating system) and the BIOS Parameter Block (BPB).
- The BPB is vital as it defines the physical and logical characteristics of the volume, such as the size of the cluster (allocation unit) and, most importantly, the exact location of the Tabella file master (MFT).
2. Master File Table (MFT)
Il Master File Table ($MFT) is the heart of the NTFS file system. It is essentially an index that records metadata for every file and directory on the volume, including the MFT itself.
- MFT Entries: Every file and folder is represented by a 1KB MFT Entry. This entry stores the file’s metadata, such as its name, security permissions, timestamps, and data location.
- Attributes: The data within an MFT entry is organized into attributes.
- Per small files, the data is stored directly within the MFT entry (a resident attribute).
- Per larger files, the MFT entry stores pointers (or “data runs”) that indicate where the file’s data is physically located on the disk (a non-resident attribute).
3. MFT Mirror ($MFTMirr)
Il MFT Mirror ($MFTMirr) is a safety feature located near the middle of the volume. It stores a copy of the first four critical entries of the MFT. If the primary MFT is corrupted, the system can use this mirror to locate the remaining MFT records and attempt to restore the file system structure.
4. System Files Area
NTFS reserves a dedicated area for special metadata files, often called System Files. These files all start with a dollar sign ($) and are crucial for the file system’s operation and integrity:
- $LogFile: Il Transactional Log File records metadata changes before they are applied to the MFT. This is essential for the system’s ability to recover consistency after a power failure or system crash (Journaling File System).
- $Bitmap: Tracks the allocation status of every cluster on the volume (whether it is free or in use).
- $Volume: Contains general information about the volume, such as its version and label.
5. Data Area
The remaining portion of the volume is the Data Area, which is where the actual file contents (data runs) are stored. The location of this data is referenced by the non-resident attributes within the MFT entries.
Core Architecture of NTFS File System
NTFS is built around a centralized metadata structure called the Tabella file master (MFT). According to Microsoft documentation, every file and directory on an NTFS volume— including system files— is represented by at least one record in the MFT.
Key architectural components include:
- Master File Table (MFT):
Acts as the index of all files and directories. Each entry contains attributes describing file name, size, timestamps, permissions, and physical disk location.
- File Attributes:
NTFS stores data as a collection of attributes rather than fixed directory entries. Common attributes include $STANDARD_INFORMATION, $FILE_NAME, and $DATA.
- Clusters and Allocation:
NTFS allocates storage in clusters, typically 4 KB by default. Files can be stored either resident (inside the MFT record) or non-resident (referenced by disk extents).
This design allows NTFS to efficiently manage large volumes and millions of files while maintaining consistent performance.
Journaling and Reliability
One of NTFS’s defining features is its journaling capability. NTFS maintains a transaction log ($LogFile) that records metadata changes before they are committed to disk.
If a system crashes or loses power:
- NTFS replays the journal during the next boot
- Incomplete metadata operations are rolled back or completed
- File system consistency is restored automatically
The good news is that journaling significantly reduces the risk of file system corruption. While it does not protect against hardware failure, it greatly improves recoverability after unexpected shutdowns.
Security and Permissions
NTFS provides advanced security mechanisms that are tightly integrated with Windows:
- Access Control Lists (ACLs):
Define precise read, write, and execute permissions for users and groups.
- Encryption (EFS):
Allows files to be transparently encrypted at the file system level.
- Ownership and Auditing:
Tracks file ownership and access events for compliance and forensic analysis.
These features make NTFS suitable for enterprise environments, but they also introduce complexity during data recovery. Professional tools must correctly interpret permissions and encrypted data to avoid further data loss.
NTFS vs FAT32 and exFAT
Compared to older file systems, NTFS offers several clear advantages:
Caratteristica | NTFS | FAT32 | exFAT |
Max file size | ~16 TB | 4 GB | ~16 EB |
Journaling | Sì | No | No |
Permissions | Sì | No | No |
Encryption | Sì | No | No |
Affidabilità | Alto | Basso | Medio |
For internal system drives, NTFS is the recommended choice. FAT32 e exFAT are typically reserved for removable media or cross-platform compatibility.
Common NTFS File System-Related Problems
Despite its robustness, NTFS volumes can still experience issues, including:
- Accidental file deletion
- File system corruption resulting in RAW status
- MFT damage due to bad sectors
- Partition table loss
- Improper disk cloning or resizing
Don’t panic if an NTFS drive becomes inaccessible. In many cases, the file data remains intact on disk even if the file system structures are damaged.
Recovering Data from an NTFS Drive
If an NTFS volume becomes inaccessible or files are missing, follow a controlled recovery process:
1. Stop using the affected drive immediately
Continued use increases the risk of overwriting recoverable data.
2. Avoid running CHKDSK automatically
While useful in some cases, CHKDSK can permanently remove damaged metadata entries.
3. Use read-only recovery software
Tools such as Magic Data Recovery analyze NTFS metadata without modifying the original drive.
4. Scan the volume and preview files
Verify recoverability before performing any restore operation.
5. Recover data to a separate storage device
Never write recovered files back to the source drive.
This methodical approach minimizes risk and maximizes recovery accuracy.
NTFS File System in Digital Forensics
NTFS is widely used in forensic investigations because it preserves:
- File creation, modification, and access timestamps
- Deleted file records in the MFT
- Alternate Data Streams (ADS)
- USN Change Journal history
These artifacts allow investigators to reconstruct file activity timelines even after deletion. From a forensic standpoint, NTFS provides significantly more evidentiary value than non-journaling file systems.
Best Practices for NTFS Users
To maintain NTFS integrity and recoverability:
- Keep regular backups
- Monitor disk health (SMART status)
- Avoid unsafe disk removal
- Use professional tools for partition changes
- Act quickly after data loss incidents
Preparation and proper response are the most effective safeguards against permanent data loss.
Conclusione
Supporta Windows 7/8/10/11 e Windows Server
FAQs About NTFS File System
1.Is NTFS good or bad?
2.Does Windows still use NTFS?
3.Does NTFS mean SSD or HDD?
4.Should I turn off NTFS?
5.What happens if I format my USB drive to NTFS?
Vasilii è uno specialista del recupero dati con circa 10 anni di esperienza pratica nel settore. Nel corso della sua carriera, ha risolto con successo migliaia di casi complessi riguardanti file cancellati, unità formattate, partizioni perse e file system RAW. La sua esperienza copre sia i metodi di recupero manuale utilizzando strumenti professionali come gli editor esadecimali, sia le soluzioni automatiche avanzate con i software di recupero. La missione di Vasilii è quella di rendere accessibile la conoscenza del recupero dati affidabile sia ai professionisti IT che agli utenti di tutti i giorni, aiutandoli a salvaguardare i loro preziosi beni digitali.



