ソリッド・ステート・ドライブ・フラッシュメモリ:仕組みとデータ復旧
目次
How Solid State Drive Flash Memory Works
To comprehend data loss and recovery, we must first explore the architecture of solid state drive flash memory. Unlike HDDs that use spinning platters and magnetic heads, SSDs store data on interconnected フラッシュメモリー chips. These chips are composed of NAND gates, organized in a complex hierarchy:
- Cells: The basic units that store bits of data. Modern SSDs use Multi-Level Cell (MLC), Triple-Level Cell (TLC), or Quad-Level Cell (QLC) technology to store multiple bits per cell, increasing density.
- Pages: Groups of cells (typically 4KB to 16KB) that are the smallest units for read and write operations.
- ブロック: Comprising many pages (e.g., 128 or 256 pages), blocks are the smallest units that can be erased. This erase-before-write cycle is a core characteristic of NANDフラッシュ.
A critical component managing this structure is the SSD controller. This processor acts as the brain of the drive, handling vital tasks such as:
- ウェア・レベリング: Distributing write and erase cycles evenly across all memory blocks to prevent premature failure of any single block.
- Garbage Collection: Identifying and consolidating valid data from partially filled blocks to free up entire blocks for new data.
- Bad Block Management: Mapping out defective memory blocks.
- Translation Layer (FTL): Creating a virtual map between the logical addresses seen by your operating system and the physical locations of data on the flash chips. This abstraction is key to SSD performance and longevity.
This sophisticated technology is why SSDs are fast and resilient to physical shock, but it also introduces unique data loss scenarios.
Common Causes of Data Loss on Solid State Drive Flash Memory
Data loss on an SSD can stem from logical issues, physical failure, or the inherent behaviors of フラッシュメモリー technology itself:
- Accidental Human Action: File deletion, formatting, or partition deletion remains the most common cause. Due to the FTL, immediately “undeleted” files have a high recovery chance.
- ファイルシステムの破損: Power outages or unsafe ejections can corrupt the file system (エヌティーエフエス, APFS, エクストラファット), causing the drive to appear as “RAW” or inaccessible.
- Firmware Failures: The SSD controller’s firmware can have bugs or become corrupted. A failed firmware update or sudden power loss during operation can “brick” the drive, making it undetectable.
- Wear-Out and Cell Degradation: Each NANDフラッシュ cell has a finite number of Program/Erase (P/E) cycles. As an SSD ages, cells can lose their ability to hold a charge reliably, leading to read errors and data corruption.
- Controller or Chip Failure: Physical damage from overheating, voltage spikes, or manufacturing defects can cause the controller or NAND chips to fail completely.
Crucially, when a file is deleted on an SSD, the トリム command (in modern systems) informs the drive that the data’s space is free. The drive may then erase those pages during garbage collection, making traditional recovery impossible. This is why acting quickly before the GC cycle is critical.
Data Recovery Strategies for Solid State Drive Flash Memory
1. Understanding Built-in and DIY Limitations
Given the complexity of solid state drive flash memory, standard OS tools have severe limitations. Windows チェックディスクまたは ファスク on macOS/Linux can repair minor file system errors but risk further data loss if the drive has physical issues. Furthermore, トリム significantly reduces the effectiveness of DIY file-carving software after deletion.
For logical issues (フォーマッティング, corruption), professional software that can interpret the FTL map and work at a low level is often necessary.
2. The Professional Recovery Approach with Magic Data Recovery
For scenarios where data is critically important, using a specialized tool designed for modern storage is advised. Magic Data Recovery employs advanced algorithms to navigate the solid state drive flash memory architecture.
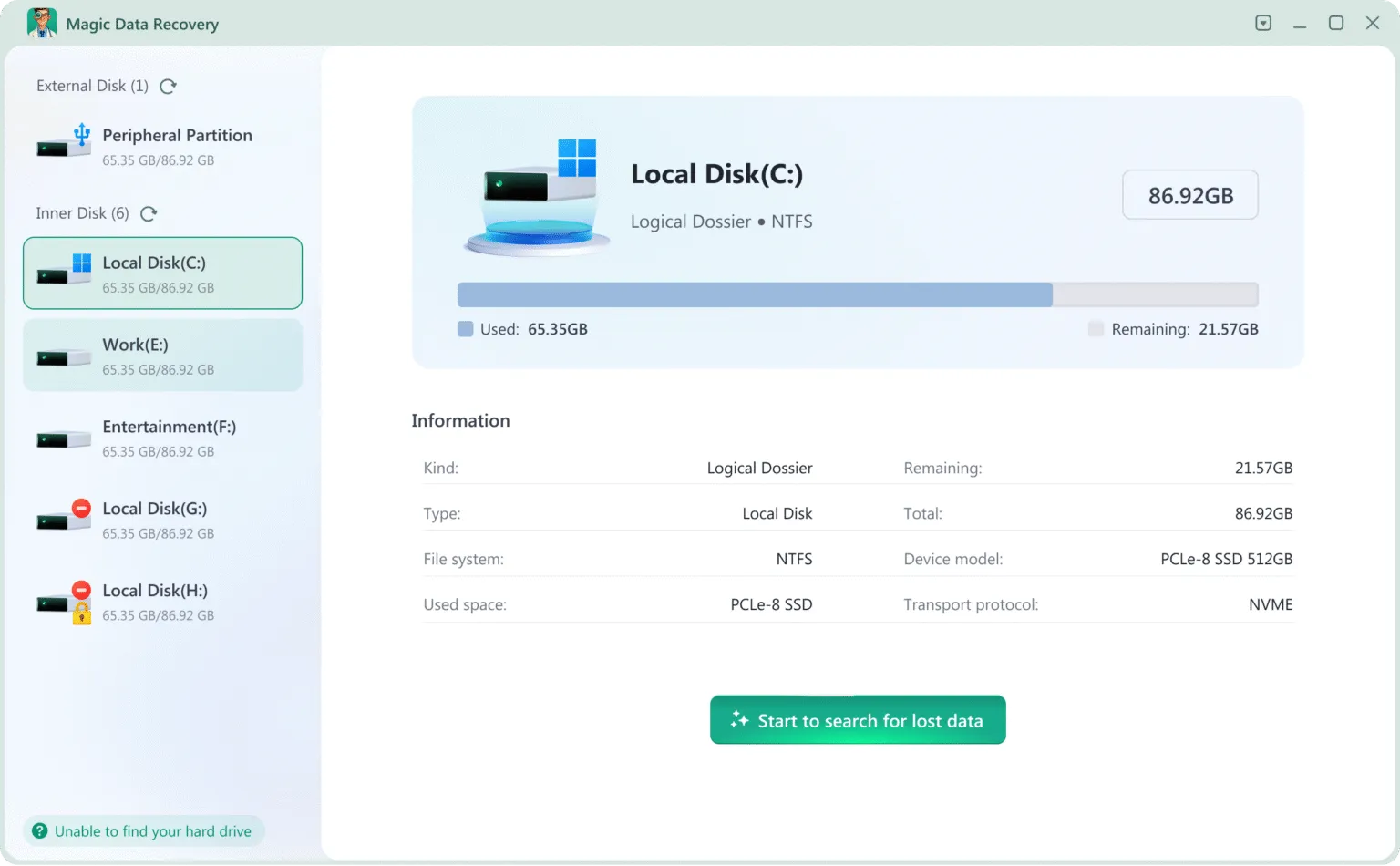
Here is a safe, step-by-step process to attempt recovery:
- Immediate Action: Stop using the affected SSD immediately to prevent overwriting.
- Create a Safe Environment: ダウンロード and install Magic Data Recovery での 違う 健康的なドライブ。.
- Connect and Select: Attach the problematic SSD (externally via a USB adapter if it’s an 内部ドライブ) and launch the software. Select the SSD from the drive list.
- Initiate a Scan: Click “Search for lost data” to start quick and deep scan. This bypasses the file system and performs a thorough analysis of the NAND flash’s accessible data structures, searching for recoverable file signatures and fragments.
- プレビューと復元: The software will display found files in a structured tree. Use the preview function to verify file integrity. Finally, select the needed files and save them to a different, secure location—never back to the source SSD.
This tool operates in a 書き込み禁止 mode, ensuring the original data on your solid state drive flash memory is not altered during the scan.
まとめ
Solid state drive flash memory represents a pinnacle of storage technology, but its complexity demands a nuanced approach to データ復旧. While the トリム command poses a challenge, timely action using appropriate methods can successfully restore data lost to formatting, corruption, or accidental deletion.
Understanding the technology empowers you to make informed decisions. For a reliable, efficient, and technically sound recovery process tailored for solid state drive flash memory, a professional-grade solution is often the most logical choice.
Take control of your data. Download Magic Data Recovery to safely scan and restore your valuable files from your SSD today.
Windows 7/8/10/11およびWindows Serverをサポート
よくあるご質問
1. Do solid state drives use flash memory?
2. What is flash memory in SSD?
3. Can data from an SSD be recovered?
4. What are the disadvantages of solid state flash drives?
5. What is the main disadvantage of an SSD?
6. What is the lifespan of an SSD drive?
7. How long do SSD flash drives last?
8. Is flash memory better than SSD?
ジェイソンは、コンピューター・データ・セキュリティ業界で15年以上の実務経験があります。データ復旧、バックアップと復元、ファイル修復技術を専門とし、世界中の何百万人ものユーザーが複雑なデータ損失やセキュリティ問題を解決できるよう支援してきました。.



