瞭解檔案和檔案系統

When a drive suddenly becomes 可望而不可及, corrupted, or unreadable, the root cause is often related to the file and file system rather than the data blocks. Don’t panic—the good news is that most situations are 邏輯問題, not physical, and can be understood and resolved with the right approach.
In practice, this article explains how files are organized on disk, how storage structures work together, the major storage formats in use, and practical methods to fix logical disk errors without risking further data loss.
目錄
What Is a File?
A 檔案 is a structured collection of data stored on a storage device. From the operating system’s perspective, a file is not just raw data—it includes 元数据 such as:
- File name
- Size
- Creation and modification timestamps
- Access permissions
- Physical location on the disk
As a result, modern operating systems do not directly manage raw disk sectors. Instead, they rely on the file system to map files to physical storage locations efficiently and safely.
What Is a File System?
A logical storage framework controls how files are stored, organized, retrieved, and managed on a storage device. It defines:
- How data blocks are allocated
- How directories are structured
- How file metadata is recorded
- How free and used space is tracked
Common file systems such as NTFS, FAT32, exFAT, 以及 EXT4 follow strict structural rules defined by operating system standards. For example, Microsoft’s NTFS relies on the 主檔案表 (MFT) to track every file and directory on the volume.
Without a functioning storage structure, data may still exist on the disk, but the operating system cannot interpret it.
File System vs. Filing System
Although often confused, these terms serve different purposes:
- File system: A technical, operating-system-level structure that manages digital data on storage media. In computing, this technical term is the correct and precise term.
- Filing system: A broader organizational method, which may include physical or digital classification systems used by humans or businesses.
Common Types of File Systems
Different operating systems and storage scenarios require different storage formats.
1. FAT32
- Widely compatible
- Limited file size (4 GB maximum)
- Minimal fault tolerance
2. exFAT
- Designed for flash storage
- Supports large files
- Common on SD cards and USB drives
3. NTFS
- Default for modern Windows systems
- Supports permissions, journaling, and encryption
- Highly resilient against corruption
4. EXT4
- Standard for Linux systems
- Efficient and stable
- Strong journaling support
Each file system balances performance, compatibility, and data integrity differently.
How Disk Structures Organize Data
Modern storage formats rely on internal structures to organize data. The most common include:
1. Hierarchical structure – Files arranged in directories and subdirectories
2. Flat structure – Minimal organization, used in simple systems
3. Indexed structure – Uses indexes to locate files quickly
4. Linked structure – Data blocks linked sequentially
5. Journaling structure – Tracks changes before committing them, reducing corruption risk
Modern file systems like NTFS and EXT4 primarily use hierarchical and journaling structures for reliability.
How to Check Disk Structure Integrity
If a drive behaves abnormally, checking the disk structure is the first safe step.
1.開啟 此電腦
2. Right-click the drive
3.選擇 屬性 → 工具 → 檢查
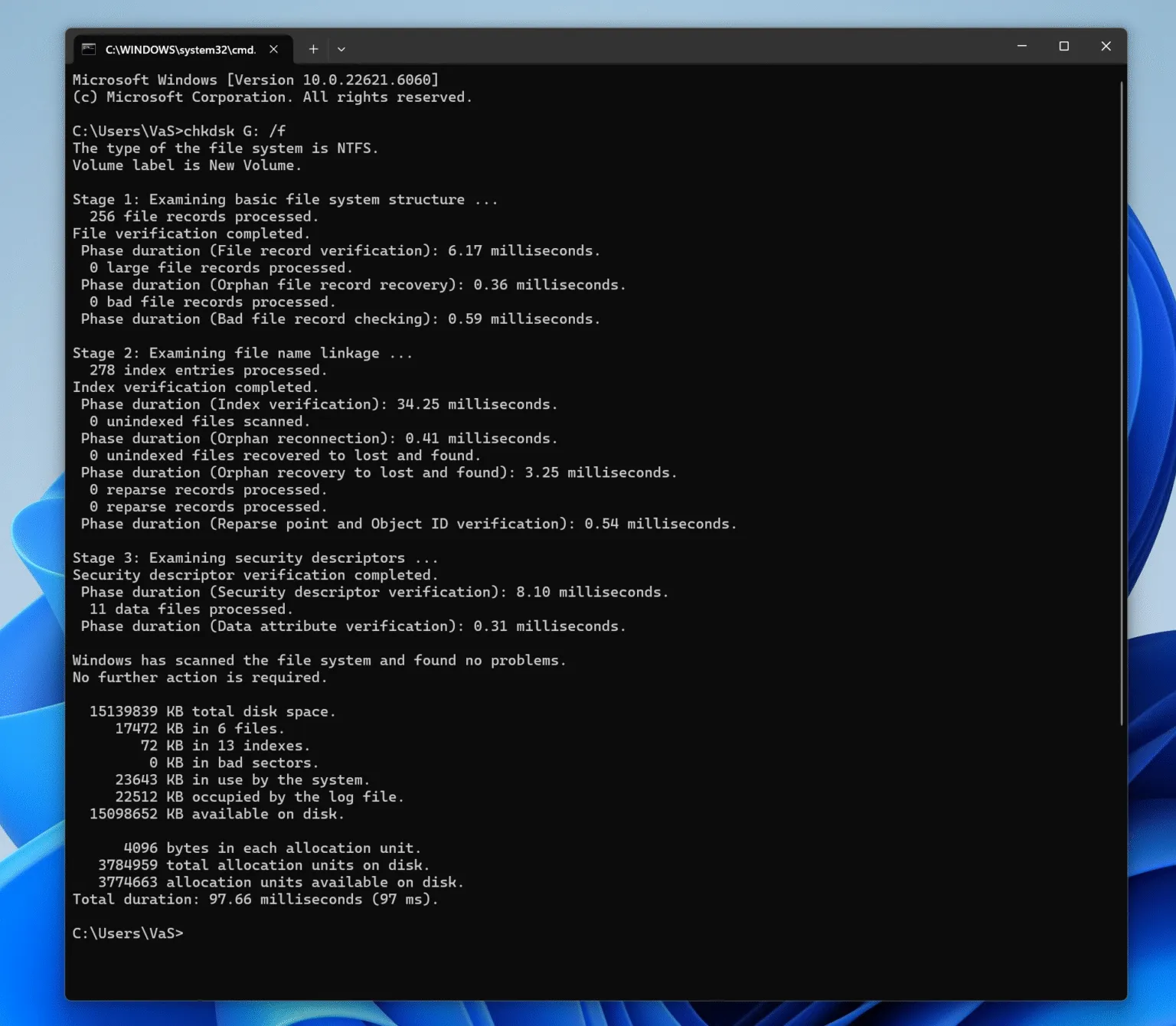
Alternatively, use Command Prompt:
chkdsk X:/f
(Replace X with the drive letter.)
This scans the logical structure for errors without modifying file content unless necessary.
How to Fix Logical Disk Errors Safely
Logical disk errors typically occur due to improper ejection, power loss, or interrupted write operations. Follow a structured approach:
Step 1: Stop Using the Affected Drive
Continued use may overwrite recoverable data.
Step 2: Identify the File System State
If the drive appears as RAW, the file structure metadata is damaged, but data often remains intact.
Step 3: Attempt Logical Repair
Use built-in tools like CHKDSK for minor issues.
Step 4: Recover Data Before Repair (Recommended)
專業工具,例如 Magic Data Recovery scan storage in read-only mode, locate disk structure records, and extract files safely—even when the underlying storage structure is corrupted or unrecognized.
This approach minimizes risk and preserves data integrity before any repair or reformatting.
Why Storage Structure Knowledge Matters for Recovery
Understanding how file systems work explains why data is often not permanently lost after 刪除, 格式化, 或 腐敗. In many cases:
- File entries are removed
- Data blocks remain untouched
- Recovery is possible until overwritten
This is why professional recovery software focuses on interpreting disk structure records rather than guessing raw data.
總結
Logical disk issues are common, manageable, and often reversible. With a clear understanding of file organization on disk and a careful recovery-first approach, you can restore access to your data safely and efficiently. Download Magic Data Recovery to scan and recover files from damaged or corrupted file systems in a secure, read-only environment.
支援 Windows 7/8/10/11 和 Windows Server
常見問題
1.What is a file and file system?
2.What is a file and filing system?
3.What are the four types of file systems?
4.Is it a file system or filesystem?
5.How do I check my file system?
6.What are the 5 file structures?
7.How to solve file system error?
Vasilii 是一位在該領域擁有約 10 年實務經驗的資料復原專家。在他的職業生涯中,他已成功解決數千個複雜的個案,包括刪除的檔案、格式化的硬碟機、遺失的磁碟分割和 RAW 檔案系統。他的專業知識涵蓋使用十六進位編輯器等專業工具的手動復原方法,以及使用復原軟體的進階自動解決方案。Vasilii 的使命是讓 IT 專業人士和一般使用者都能獲得可靠的資料復原知識,協助他們保護寶貴的數位資產。.



