Data Fabric
Table of Contents
Hybrid Storage Without the Spaghetti
Most organizations now mix local servers, cloud buckets, SaaS databases, and archived snapshots.
Engineers wire them together with one-off scripts, custom ETL jobs, and many dashboards.
Eventually the environment turns into a spaghetti diagram that no one fully understands.
A data fabric addresses that problem by acting as a unified layer over all those storage resources, whether they live on-premises or in multiple clouds.
Defining Data Fabric in Modern Architectures
A data fabric is an architectural approach, not a single product.
Vendors implement it in different ways, yet the core idea stays consistent: create a logical layer that connects, secures, and manages data across hybrid and multi-cloud locations.
Instead of copying everything into one giant warehouse, you build:
A consistent way to discover data assets
A set of shared services (security, governance, transformation)
A virtual view that hides physical complexity from most consumers
Because of this abstraction, applications and analytics tools query through the fabric while the fabric orchestrates where and how to access underlying storage.
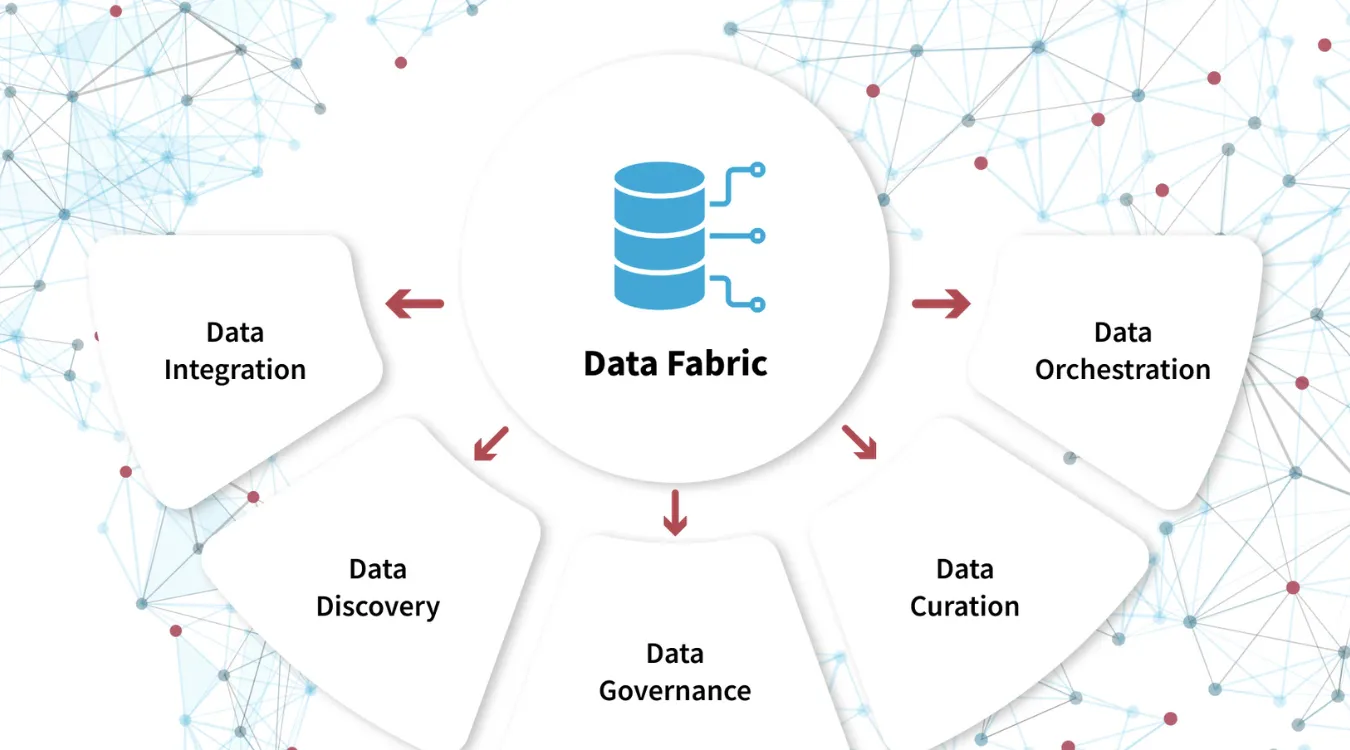
Key Capabilities Woven Into a Data Fabric
Although implementations differ, successful fabrics usually provide several capabilities.
Unified Access and Virtualization
A fabric exposes data through common interfaces, such as SQL endpoints, APIs, or catalogs.
It can present tables and objects from many systems as if they belonged to one logical space.
Consequently, analysts focus on datasets and policies instead of connection strings and credentials for each silo.
Integrated Governance and Security
Security and governance often scatter across tools.
A data fabric centralizes:
Access control and policies
Masking and tokenization rules
Lineage and usage tracking
As a result, auditors can trace how sensitive fields move, and administrators can apply consistent rules without rewriting every pipeline.
Intelligent Movement and Caching
The fabric decides when to move data, when to leave it in place, and when to cache results.
Sometimes it ships queries to where data already lives.
Sometimes it materializes results near the users or near heavy processing engines.
This flexibility reduces unnecessary copies while still meeting performance and locality requirements.
Data Fabric in Relation to Data Mesh and ETL
Because buzzwords overlap, it helps to compare them directly.
Architecture and Ownership View
Data fabric focuses on a unified technical layer and shared services.
Data mesh emphasizes domain ownership, product thinking, and federated governance.
You can, in fact, run a mesh of domain data products on top of a fabric that provides connectivity, catalogs, and security.
Movement and Transformation View
ETL still matters inside a fabric.
Pipelines extract, transform, and load when you need permanent derived datasets or performance-optimized stores.
However, the fabric adds:
Discovery of existing data before you build new flows
On-demand, virtualized access where copying becomes optional
Global policies that ETL jobs must respect
Therefore, ETL becomes one tool inside a broader fabric rather than the only way data moves.
Quick Comparison Table
| Aspect | Data Fabric | Data Mesh | Classic ETL |
|---|---|---|---|
| Main focus | Unified data layer & services | Domain ownership & data products | Movement & transformation |
| Scope | Hybrid / multi-cloud connectivity | Org structure and responsibilities | Specific pipelines |
| Data location | Mix of in-place and moved | Depends on domain decisions | Mostly moved to targets |
| Governance | Central platform capabilities | Federated across domains | Often pipeline by pipeline |
When a Data Fabric Helps the Most
A data fabric fits environments with real diversity and scale.
It adds value when:
Data spreads across several clouds and on-premises stores
Teams run many tools that all need overlapping datasets
Security and compliance rules must apply consistently
Copying large volumes between platforms has become expensive
Conversely, a small organization with a single primary database and a few reports may not benefit much from the complexity.
Impact on Backup, Recovery, and Data Resilience
From a data protection angle, a fabric changes how you think about resilience.
You no longer protect just one central store; you protect an interconnected layer of many stores, snapshots, and replicas.
A fabric-aware protection approach:
Tracks where critical datasets live across platforms
Coordinates backups and retention policies from one view
Uses catalogs and metadata to recover the correct version in the correct place
When parts of the fabric fail or stores become corrupted, tools such as Amagicsoft Data Recovery still help at the volume level.
However, fabric metadata and lineage speed up the task of locating which copies matter and where to restore them.
Supports Windows 7/8/10/11 and Windows Server.
Supports Windows 7/8/10/11 and Windows Server
Operating and Evolving a Data Fabric
Designing a fabric is not a one-time project.
It evolves with systems, regulations, and analytics needs.
Practical steps include:
Start with high-value domains instead of the entire enterprise.
Standardize metadata conventions and ownership early.
Integrate logging and monitoring for data access patterns.
Regularly review which datasets justify physical copies versus virtual access.
Keep a clear catalog entry for every backup, archive, and recovery dataset that plugs into the fabric.
Over time, this discipline turns your hybrid storage estate into a navigable, governed space instead of a collection of isolated islands.
FAQ
What is meant by data fabric?
When to use data fabric?
What are the disadvantages of data fabric?
What is data fabric vs mesh?
Is DS easier than CS?
Is data fabric the future?
What is the difference between data fabric and ETL?
What are the 4 pillars of data mesh?
Which is better, mesh or fabric?
Which mesh fabric is best?
Eddie is an IT specialist with over 10 years of experience working at several well-known companies in the computer industry. He brings deep technical knowledge and practical problem-solving skills to every project.