Full Format: How It Works, Data Recovery Chances, and Best Practices

Table of Contents
Introduction
Formatting a storage device looks simple, but the choice you make can permanently affect your data. Many users select Full Format when fixing disk errors, reinstalling an operating system, or preparing a drive for resale. However, few fully understand what happens during the process or whether files can still be recovered afterward.
This guide explains Full Format in plain language. You will learn how it works internally, how to use it correctly, how it compares with Quick Format, and what realistic recovery options exist after formatting. If data loss has already occurred, this article also explains when data recovery software like Magic Data Recovery may still help—and when expectations should remain conservative.
What Is Full Format?
It is a disk formatting method that completely prepares a storage device for reuse by rebuilding the file system and scanning the entire disk surface for errors.
Unlike Quick Format, it does more than reset file system metadata. It checks each sector of the drive and marks damaged sectors as unusable. On modern Windows systems, it also writes zeros to accessible sectors, which significantly reduces the chance of data recovery.
Users commonly apply Full Format when:
- Fixing persistent disk errors
- Cleaning a drive before resale or disposal
- Preparing a drive for a fresh operating system installation
- Verifying disk health on older or unreliable drives
Because of its depth, the complete format takes much longer and has a much stronger impact on existing data.
How The Format Works (Formatting Principle Explained)
To understand why data recovery becomes difficult after Full Format, it helps to look at the process step by step.
1. File System Reinitialization
The formatting process rebuilds the file system structure, such as NTFS or FAT32. File tables, indexes, and directory mappings are recreated from scratch.
2. Sector-by-Sector Scan
The system scans every sector on the disk to detect physical errors. Any problematic sectors are marked to prevent future use.
3. Data Overwriting (Zero Writing)
On modern Windows versions, the formatting writes zeros to all readable sectors. This overwriting action destroys the original data content rather than just hiding it.
4. Disk Validation
The operating system ensures the disk is usable, stable, and error-free before completing the process.
Because of these steps, Full Format is both a formatting and verification operation.
How to Perform a Full Format Safely
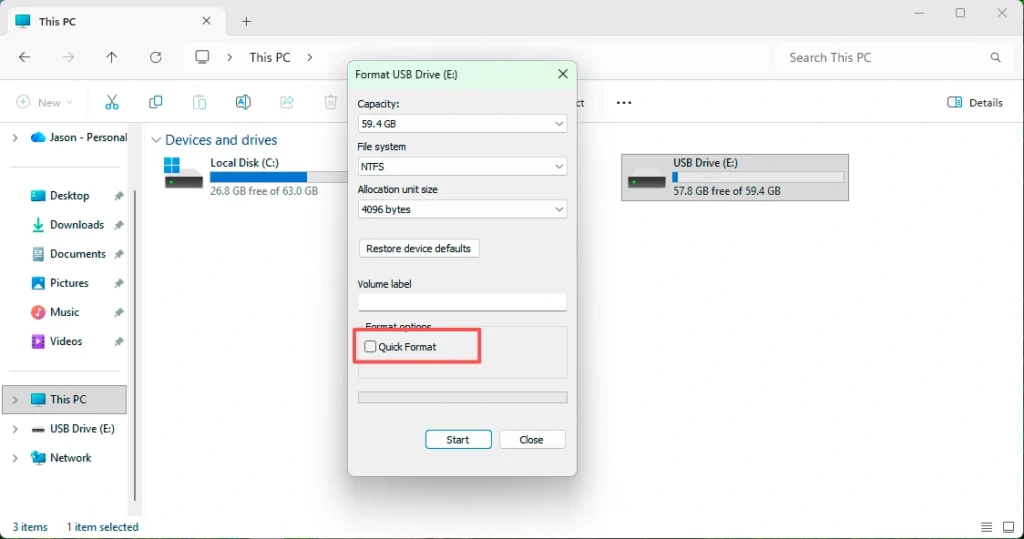
Format in Windows Disk Management
- Open Disk Management
- Right-click the target partition
- Select “Format”
- Uncheck “Quick Format”
- Choose a file system and start formatting
Format Using Command Prompt
- Use the
formatcommand without the/qparameter - This forces a complete format instead of a quick one
Best Practices Before Formatting
- Disconnect other storage devices
- Double-check the selected drive letter
- Avoid formatting if you suspect hidden data loss issues
Full Format vs Quick Format (Comparison Table)
Feature | Full Format | Quick Format |
Scans disk sectors | Yes | No |
Writes zeros | Yes (modern OS) | No |
Detects bad sectors | Yes | No |
Time required | Long | Very short |
Data recovery chance | Very low | High |
Recommended use | Disk cleanup, resale | Fast reuse |
This comparison shows why Full Format offers stronger data removal but lower recovery possibilities.
Data Recoverability After Full Format
Is Data Recoverable After Full Format?
In most cases, data recovery after formatting is extremely difficult. The zero-writing process destroys file contents, not just file references.
However, limited recovery may still be possible under specific conditions:
- Formatting stopped prematurely
- Some sectors were not overwritten
- Data existed on another partition or external drive
What Can Still Be Tried?
Although success rates remain low, scanning the drive with professional data recovery software may detect:
- Unoverwritten fragments
- Files stored in unaffected partitions
- Data cached on external or secondary disks
This approach does not guarantee results, but it offers a final chance before giving up.
When to Use Magic Data Recovery After Format
Core Problem It Solves
Users often feel helpless after formatting, especially when critical files disappear instantly. Magic Data Recovery helps by scanning storage devices at a deep level to locate recoverable data remnants.
Supports Windows 7/8/10/11 and Windows Server
Key Advantages
- Advanced sector-level scanning
- Support for formatted drives
- Preview before recovery
- Read-only operation to avoid further damage
Practical Use Cases
- Accidental Full Format on the wrong partition
- Data loss during OS reinstallation
- Unexpected formatting caused by disk errors
Why It Is More Reliable
Unlike basic recovery tools, Magic Data Recovery focuses on safe scanning and file integrity detection. It does not claim unrealistic recovery rates and works best when used immediately after formatting.
If you are searching for a practical solution after formatting, Magic Data Recovery is worth trying before concluding that the data is permanently lost.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Formatting the wrong drive
- Reusing the disk before recovery attempts
- Installing recovery software on the formatted drive
- Expecting full recovery after zero overwriting
Avoiding these mistakes improves recovery odds, even after the format.
Conclusion
Full Format is a powerful but irreversible operation designed to fully clean and verify a storage device. It differs significantly from Quick Format by scanning sectors and overwriting data, which explains the low recovery success rate.
Although data recovery after formatting remains challenging, tools like Magic Data Recovery can still help identify unoverwritten fragments or data stored elsewhere. For users facing accidental formatting, acting quickly and choosing the right tool makes a measurable difference.
If you need a careful, professional recovery attempt after formatting, Magic Data Recovery provides a reliable and transparent option.
Supports Windows 7/8/10/11 and Windows Server
FAQs
1. What is the full format?
2. When to do full format?
3. Is a full format worth it?
4. Does full format write zeros?
5. How long is a full format?
6. What is the full meaning of format?
Erin Smith is recognized as one of the most professional writers at Amagicsoft. She has continually honed her writing skills over the past 10 years and helped millions of readers solve their tech problems.



