Disk Management: How to Use, Fix Disk Issues

When a hard drive or SSD suddenly becomes inaccessible, many users first notice something is wrong inside Disk Management. Partitions may disappear, turn RAW, or show errors such as “Unallocated” or “Unknown.” At this point, panic often sets in—especially if important data is stored on the disk.
This guide explains Disk Management in plain language. You will learn how it works, what different disk states mean, how it differs from Device Manager, and—most importantly—how to recover lost data from an SSD when disk issues occur. Practical recovery solutions, including Magic Data Recovery, are introduced naturally based on real-world scenarios.
Table of Contents
What Is Disk Management?
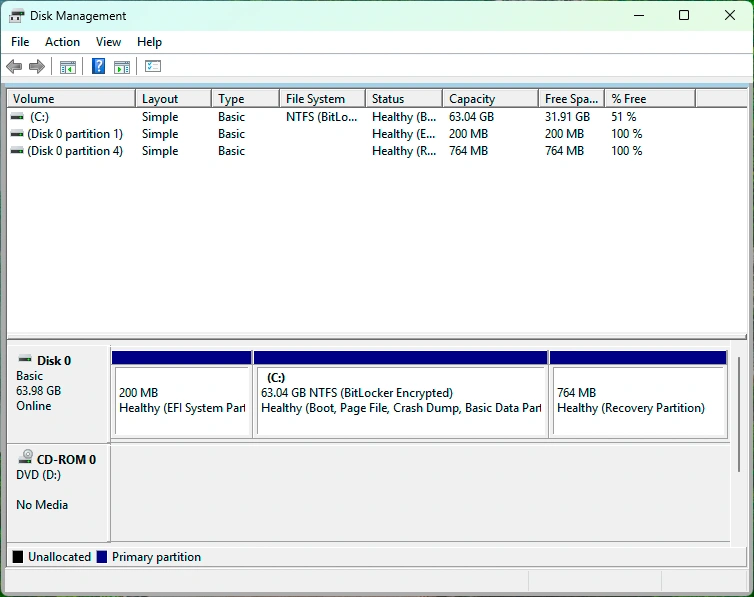
It is a built-in Windows utility that allows users to view, manage, and configure storage devices connected to their system. It provides a graphical overview of all disks, partitions, file systems, and volume statuses.
Unlike File Explorer, Windows disk drive management shows low-level disk information. This makes it essential for diagnosing storage problems, creating or deleting partitions, and preparing new drives for use.
Key Functions
- Initialize new HDDs or SSDs
- Create, format, extend, or shrink partitions
- Assign or change drive letters
- Detect disk errors and abnormal states
- Display file system types such as NTFS, FAT32, or RAW
For both everyday users and IT professionals, Disk Management is often the first tool used when a disk does not behave as expected.
The Role and Purpose of Disk Management
The primary role of Disk Management is disk-level control rather than file-level access. It helps users understand how storage is structured and whether the operating system can correctly communicate with the disk.
In practice, Disk Management is used to:
- Troubleshoot missing or inaccessible drives
- Prepare SSDs for system installation
- Rebuild partition layouts after disk changes
- Identify potential data loss risks before they escalate
For example, when an SSD suddenly shows as “Unallocated,” Disk Management confirms that the partition table has been damaged—even if the data itself still exists.
Common Disk States in Disk Management
Understanding disk states is critical before taking action. Incorrect operations, such as formatting the wrong partition, can permanently erase data.
Healthy (Primary Partition)
This status indicates that the partition is working correctly and has a recognized file system. Data is accessible, and no immediate action is required.
Unallocated
Unallocated space means that the partition structure is missing. This often occurs after accidental deletion, disk corruption, or partition table damage.
Important note:
Unallocated does not mean the data is gone. In many cases, files can still be recovered.
RAW
A RAW partition indicates that Windows cannot recognize the file system. This may result from file system corruption, unsafe removal, power failure, or SSD controller errors.
Do not format a RAW partition if data is important.
Offline
The disk is detected but not accessible. This can happen due to signature conflicts or manual offline settings.
Unknown / Not Initialized
Windows recognizes the physical disk but cannot read its structure. Initialization prompts often appear, but initializing the disk may overwrite critical metadata.
Disk Management vs Device Manager
Although both tools are part of Windows, Disk Management and Device Manager serve very different purposes.
Feature | Disk Management | Device Manager |
Focus | Partitions & volumes | Hardware & drivers |
File system visibility | Yes | No |
Data recovery relevance | High | Low |
SSD/HDD initialization | Yes | No |
In short, Device Manager confirms whether hardware is detected, while Disk Management determines whether data structures are readable. When dealing with partition loss or RAW errors, Disk Management is the correct diagnostic tool.
How to Recover Lost Data from Drive Issues
Drive data loss scenarios often appear first in Disk Management. Below are common cases and the correct recovery approach.
Scenario 1: Partition Missing or Deleted
If a partition disappears and the space becomes unallocated:
- Stop writing data immediately
- Do not create a new partition
- Avoid disk initialization
A specialized recovery tool is required to scan the SSD and reconstruct lost partitions.
Scenario 2: Partition Turns RAW
When a partition shows RAW:
- Formatting will erase file system metadata
- CHKDSK usually fails on RAW partitions
In this case, file-level recovery is the safest option.
Scenario 3: Partition Error or File System Corruption
File system errors may result from sudden shutdowns or SSD firmware issues. While Windows repair tools may help, they often fail when corruption is severe.
Why Magic Data Recovery Is Recommended for Data Recovery
When Disk Management shows critical disk issues, Magic Data Recovery offers a practical and reliable solution without risking further damage.
Core Problems It Solves
- Recovers data from RAW, unallocated, or deleted partitions
- Supports HDDs, SSDs, NVMe drives, and external storage
- Works even when it cannot mount the drive
Key Advantages
- Read-only scanning prevents data overwriting
- Advanced algorithms optimized for SSD structures
- Supports common file systems used on Windows
- Clear preview before recovery improves accuracy
Real-World Use Case
A common scenario involves an SSD that suddenly shows as RAW after a system crash. Disk Management detects the disk but cannot access files. Using Magic Data Recovery, users can scan the SSD, preview important documents, and restore them safely to another drive.
Compared to manual fixes or risky formatting, this approach significantly reduces data loss risks.
If you are looking for a safer and more efficient solution, Magic Data Recovery is worth considering.
Supports Windows 7/8/10/11 and Windows Server
Best Practices Before Using Disk Management to Fix Issues
Before taking any corrective action in Disk Management, follow these guidelines:
- Never format a disk with important data
- Avoid repeated initialization attempts
- Stop using the affected SSD immediately
- Perform recovery before repair operations
These steps increase the success rate of data recovery significantly.
Conclusion
Disk Management is a powerful diagnostic tool, but it is not a data recovery solution. It helps identify problems such as missing partitions, RAW file systems, and disk errors. However, incorrect actions inside Disk Drive Management can worsen data loss.
For SSD-related issues, especially when data matters, using a dedicated recovery tool like Magic Data Recovery provides a safer and more reliable path. It addresses the core pain points without destructive operations, making it a trusted choice for both everyday users and professionals.
FAQs About Disk Management
1. What is Disk Management used for in Windows?
2. Why does my SSD show RAW in Disk Management?
3. Can Disk Management recover lost data?
4. Is it safe to initialize a disk in Disk Management?
5. How do I fix an unallocated SSD without losing data?
6. Does Magic Data Recovery work with SSDs?
7. What should I do first when Disk shows errors?
Erin Smith is recognized as one of the most professional writers at Amagicsoft. She has continually honed her writing skills over the past 10 years and helped millions of readers solve their tech problems.