フラッシュメモリー

目次
Flash Memory in Everyday Storage
USB flash drives, SD cards, SSDs, and many embedded devices all rely on flash memory.
When these devices fail, users often believe the data disappeared forever.
In reality, flash chips often still contain user data after deletion, formatting, or file system errors.
With the right workflow, many files on flash-based storage still leave room for safe recovery.

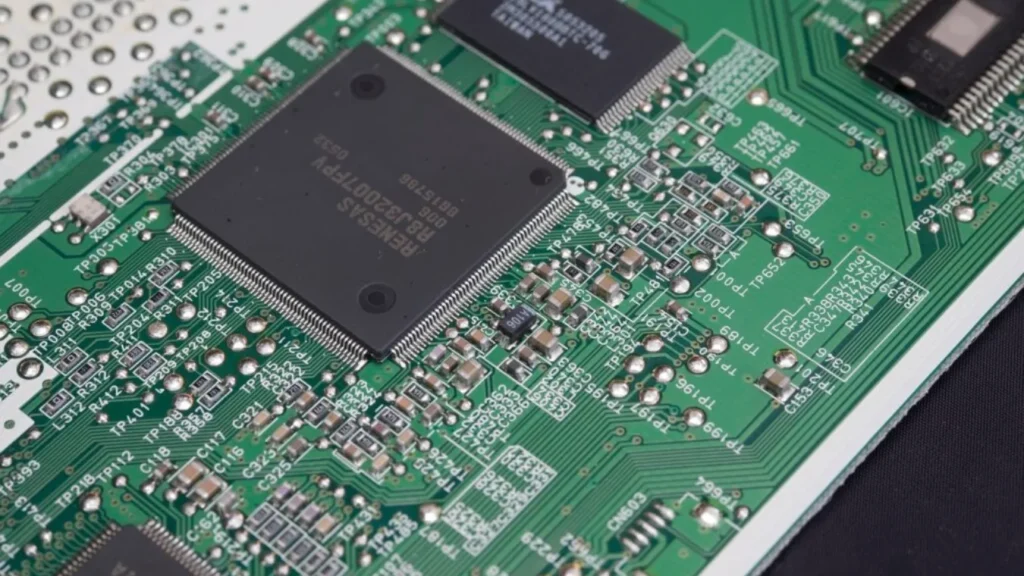
How Flash Memory Stores Data Electronically
Flash memory uses arrays of floating-gate transistors.
Each cell holds electrons inside an insulated gate and represents a bit or multiple bits.
Key concepts:
Cells and pages: The controller reads and writes data by page.
Blocks: The controller erases data by block, not by individual page.
Program/erase cycles: Each cell tolerates only a limited number of erase cycles.
The memory controller translates logical block addresses from the operating system into physical locations on the chip.
This translation layer enables wear-leveling and bad-block management.
Types of Flash Memory and Where They Appear
Different flash technologies trade speed, cost, and endurance.
| タイプ | Bits per Cell | 代表的な使用例 | 強み | 制限事項 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SLC | 1 | Industrial, enterprise cache | High endurance, fast writes | High cost per GB |
| MLC | 2 | Consumer SSDs, pro USB drives | Good balance of cost and life | Moderate endurance |
| TLC | 3 | Most consumer SSDs, SD cards | Low cost, high capacities | Lower endurance, slower writes |
| QLC | 4 | High-capacity SSDs, archives | Very low cost per GB | Reduced write endurance |
Many consumer flash devices use TLC or QLC and rely heavily on controller algorithms to maintain acceptable performance and lifespan.
Flash Memory vs. RAM and SSDs
Flash memory often creates confusion because users see similar terms across products.
Flash Memory vs. RAM
Random access memory (RAM) holds data only while power stays on.
Flash memory retains data without power, so devices can store files and firmware.
RAM focuses on speed and supports frequent reads and writes.
Flash focuses on non-volatile storage and handles slower write and erase cycles with more care.
Flash Memory vs. SSD
An SSD uses flash memory plus a dedicated controller, firmware, cache, and interface logic.
In other words, an SSD behaves like a complete storage device, not just raw memory.
USB drives and SD cards also wrap flash chips with controllers, but they target removable, lower-cost storage.
SSDs focus on higher performance, stronger error correction, and more advanced wear-leveling.
Why Data Still Exists After Deletion or Formatting
When you delete files on flash-based storage, the system usually marks clusters as free.
The controller and file system still retain the underlying data until new writes reuse those locations.
Quick formats often recreate file system structures and leave most content untouched.
Only secure erase operations or heavy new writes actually overwrite most of the old data.
Because of this behavior, データ復旧ソフト can still scan raw space, read file system metadata, and rebuild many files.
Typical Data Loss Scenarios with Flash Memory
Flash devices fail in recognizable ways.
Understanding the pattern helps users choose an appropriate recovery strategy.
Common scenarios include:
Accidental deletion of files and folders
Quick format of a USB drive or SD card
File system corruption after unsafe removal
“Please format the disk” prompts in Windows
RAW file system status in Disk Management
Controller failures that cause random errors or no detection
Logical problems (deletion, format, file system damage) often allow software-based recovery.
Severe controller or chip damage requires hardware-level work in a specialized lab.
Advanced View: Controller Behavior, Wear-Leveling, and TRIM
Flash controllers constantly move data around.
They do this to spread wear across blocks and to avoid repeated writes to the same cells.
Important mechanisms:
Wear-leveling: Evenly distributes program/erase cycles across blocks.
Garbage collection: Consolidates valid pages and frees entire blocks for erasure.
Error correction (ECC): Detects and corrects bit errors that arise over time.
トリム: The operating system signals which blocks no longer hold live data.
These mechanisms improve performance and lifetime but also complicate recovery.
Raw images from flash devices do not always match the logical layout that the operating system sees.
Safe Strategy Before Flash Recovery
Users should prepare flash devices carefully before scanning.
Stop writing to the device immediately.
Avoid running file system repair tools such as quick format or generic “fix” utilities.
Connect the flash drive, SD card, or SSD to a stable computer.
Verify that Windows detects the device in Disk Management.
If the device drops in and out, or the system reports repeated I/O errors, recovery attempts must proceed carefully.
In critical cases, experienced technicians often image the device first and then analyze the image.
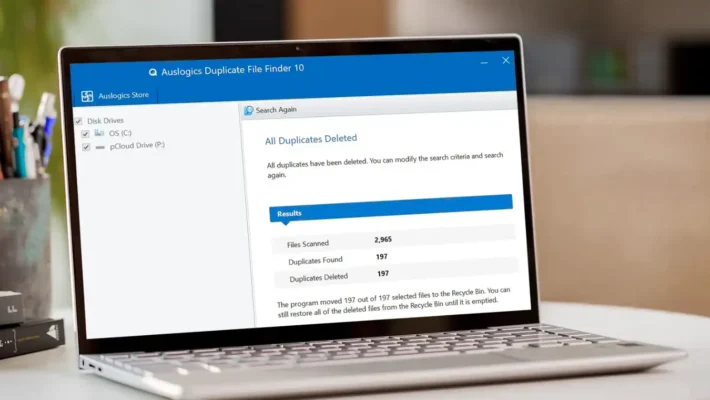
Software-Based Flash Recovery with Amagicsoft
For many logical failures on USB drives, SD cards, and SSDs, software offers a practical solution.
Amagicsoftデータ復旧 helps general users scan flash-based storage in a read-only manner and copy recoverable files to a safe destination.
You should always recover data to another disk or partition.
This approach avoids further overwrites on the failing device.
Step-by-Step: Recovering Lost Files from Flash Media
Follow this process when Windows still detects the flash device.
1. Prepare the Environment
Use a healthy computer with enough free storage for recovered files.
Connect the flash drive, SD card (through a reader), or SSD.
Confirm that the drive appears, even if Windows marks it as RAW or unformatted.
2. Install and Start Amagicsoft Data Recovery
ダウンロード Amagicsoftデータ復旧 and install it on a system drive or another healthy disk.
打ち上げ Amagicsoftデータ復旧.
Wait for the software to list all available storage devices.
3. Choose the Flash Device and Scan
Select the problematic flash device as the scan source.
Use a クイックスキャン when you deleted files recently.
選ぶ ディープ・スキャン when formats, RAW file systems, or severe corruption appear.
Start the scan and allow it to complete.
4. Review, Filter, and Preview Files
Filter results by type, such as documents, photos, or videos.
Browse reconstructed folders and check familiar paths like DCIM on SD cards or 書類 on USB drives.
Use the preview feature to verify that important files still contain valid content.
5. Recover to a Safe Target
Select the files and folders you want to restore.
Choose a different physical drive as the recovery destination.
Start the recovery process.
Open several recovered files and confirm that they work as expected.
After you secure the data, you can reformat or replace the flash device based on its health and age.
Amagicsoftデータ復旧 supports Windows 7/8/10/11 and Windows Server.
Windows 7/8/10/11およびWindows Serverをサポート
Practical Tips to Extend Flash Memory Life
Flash memory does not last forever, but good habits extend its usable lifespan.
Eject flash drives safely before removal.
Avoid full-capacity operation for long periods.
Keep only one or two active write-heavy workloads on a flash device.
Maintain regular backups to another drive or cloud service.
Replace aging USB drives and memory cards before they fail during critical work.
まとめ
Flash memory enables compact, silent, and efficient storage across many devices.
It stores data electronically in cells and depends on complex controller logic to manage wear and integrity.
When data loss occurs, users should stop writes, connect the device to a stable system, and rely on specialized tools.
Amagicsoftデータ復旧 offers a controlled, step-by-step way to recover files from flash-based storage without unnecessary risk.
With the right workflow, many “lost” files on flash media still remain within reach.
よくある質問
What do you mean by flash memory?
Is flash memory the same as RAM?
What is flash memory vs SSD?
How long will data stay on a flash drive?
Can flash memory be recovered?
What is the lifespan of a flash memory?
Can flash memory be erased?
How do I fix my flash memory?
エディは、コンピューター業界の有名企業数社で10年以上の経験を持つITスペシャリストです。深い技術的知識と実践的な問題解決能力をすべてのプロジェクトに提供しています。.