What is NAND Flash Memory?

Table of Contents
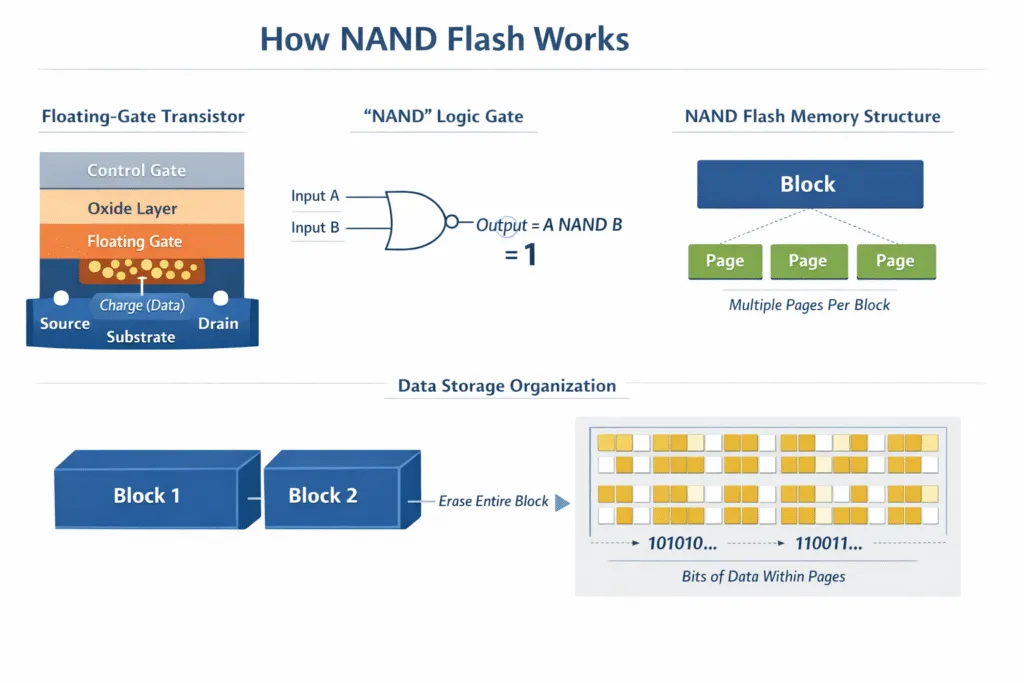
How NAND Flash Memory Works
Main Flash Cell Technologies
SLC (Single-Level Cell)
Stores one bit of data per cell. SLC is the fastest and most reliable type of NAND flash, but it is also the most expensive and typically used in high-end applications.
MLC (Multi-Level Cell)
Stores two bits of data per cell, providing higher density but slower speeds and lower durability compared to SLC.
TLC (Triple-Level Cell)
Stores three bits of data per cell, offering even higher storage capacity at a reduced cost, but with further compromises in speed and lifespan.
QLC (Quad-Level Cell)
Stores four bits of data per cell, optimizing storage capacity at the cost of even lower endurance and speed.
Key Benefits
Durability: NAND flash is resistant to physical shocks and vibrations, making it suitable for portable devices and rugged environments.
Speed: Provides fast read and write speeds, significantly improving system performance, particularly in SSDs and memory cards.
Low Power Consumption: Lower power consumption helps extend battery life in mobile devices.
Compact Size: NAND flash memory modules are small and lightweight, enabling use in compact devices such as smartphones and tablets.
Limitations of NAND Flash
Limited Write Cycles: Each memory cell in NAND flash has a finite number of write and erase cycles. While modern NAND flash is designed to handle millions of cycles, wear and tear over time can lead to performance degradation.
Data Retention: Though NAND flash retains data when power is off, its ability to do so can diminish over time, especially in high-temperature environments.
Performance Variability: The performance of NAND flash can degrade when the storage becomes nearly full, as the system performs more complex data management tasks to free up space.
Common Applications
Solid-State Drives (SSDs): SSDs utilize NAND flash memory to provide faster data access, improving overall system performance and reducing boot times.
USB Drives and SD Cards: NAND flash is the standard storage technology in USB flash drives and SD cards, making it essential for portable storage solutions.
Smartphones and Tablets: Most mobile devices rely on NAND flash for internal storage, offering quick access to apps, files, and media.
Best Practices and Tips for Using NAND Flash:
- Regular Backups: Due to the limited write cycles, it’s important to back up data regularly to prevent permanent loss if the storage device fails.
- Avoid Filling Storage to Capacity: Keeping storage usage below 80% can help maintain NAND flash performance and extend its lifespan.
- Temperature Control: High temperatures can accelerate wear on NAND flash. Always store devices in a cool environment and avoid exposing them to extreme heat.
Conclusion
Supports Windows 7/8/10/11 and Windows Server
FAQ
1.What is NAND flash memory?
2.Is SSD NAND flash memory the same?
3.Does NAND flash memory last forever?
4.Is flash memory better than SSD?
5.Do SD cards use NAND flash?
6.Which is better, NAND or NOR flash?
7.Is NAND the same as eMMC?
Vasilii is a data recovery specialist with around 10 years of hands-on experience in the field. Throughout his career, he has successfully solved thousands of complex cases involving deleted files, formatted drives, lost partitions, and RAW file systems. His expertise covers both manual recovery methods using professional tools like hex editors and advanced automated solutions with recovery software. Vasilii's mission is to make reliable data recovery knowledge accessible to both IT professionals and everyday users, helping them safeguard their valuable digital assets.



