FAT File System: A Complete Understanding

Although modern operating systems support advanced storage formats, the FAT file system remains widely used—especially on removable media such as USB flash drives, SD cards, and embedded devices. Its continued relevance comes not from advanced features, but from simplicity and universal compatibility.
Unlike newer designs that rely on complex metadata structures, FAT focuses on minimal overhead. As a result, devices with limited resources can implement it easily, and different operating systems can recognize it without additional drivers.
Table of Contents
What “FAT” Means in Storage Design
FAT stands for File Allocation Table, which describes the core mechanism used to track stored data. Instead of maintaining large metadata records, the system uses a table to record how disk clusters connect to each other.
Each entry in this table points to the next cluster in a file’s sequence or marks the end of the file. Because of this design, the operating system can locate file data by following a simple chain rather than interpreting complex structures.
This approach favors clarity and speed over resilience.
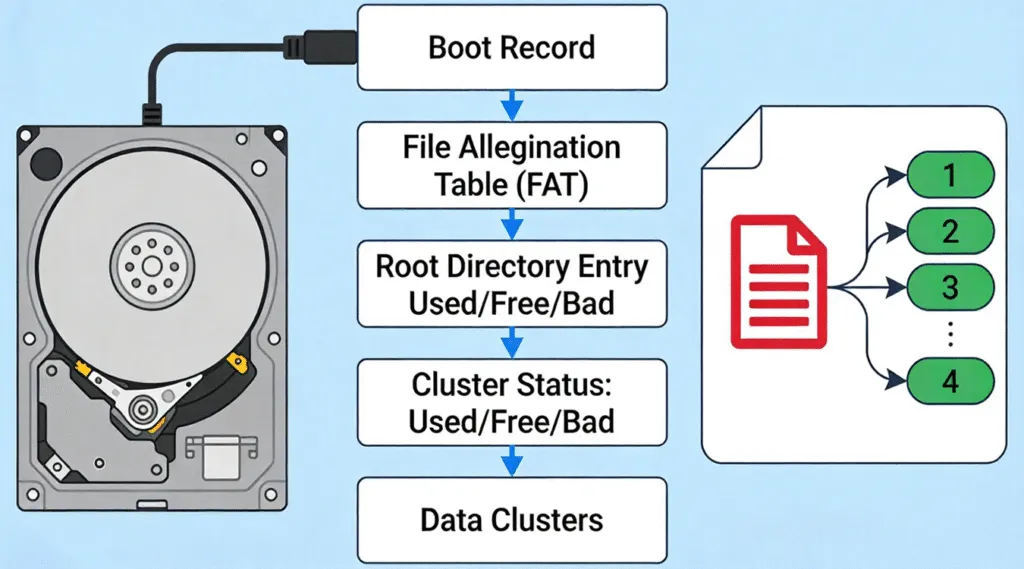
How Data Is Organized in a FAT File System
A FAT-formatted storage device follows a straightforward layout:
- Boot sector – Contains basic information required to mount the volume
- File Allocation Table – Tracks cluster usage and file chains
- Root directory – Stores file and folder entries
- Data area – Holds actual file content
When you create a file, the system allocates available clusters and records their order in the table. When you delete the file, those entries are marked as free, although the underlying data often remains until overwritten.
FAT Variants and Their Differences
Over time, several FAT versions have emerged to address growing storage needs.
FAT16
Designed for early storage devices, FAT16 supports small volumes and is rarely used today.
FAT32
Introduced to support larger disks, FAT32 became the most common variant. However, it enforces a maximum file size of 4 GB, which limits its usefulness for modern media files.
exFAT
While technically a separate design, exFAT evolved from FAT principles. It removes the 4 GB file size limit and performs better on flash storage, making it common on SDXC cards.
Each variant maintains the core simplicity that defines FAT-based systems.
Strengths of the FAT File System
The design offers several practical advantages:
- Extremely wide compatibility across operating systems and devices
- Low processing overhead
- Simple implementation for firmware and embedded systems
- Fast access on small or removable storage
Because of these traits, manufacturers often choose FAT for devices that must work immediately when connected.
Limitations You Should Understand
Despite its strengths, FAT has important limitations.
It does not support:
- File permissions or access control
- Journaling or crash recovery
- Strong corruption resistance
Additionally, fragmentation occurs more easily because the system does not optimize cluster placement aggressively. As storage sizes grow, these weaknesses become more noticeable.
What Happens When FAT File System Become Corrupted
When table entries or directory records are damaged, the operating system may lose the ability to follow file chains correctly. Consequently, files may appear missing, truncated, or unreadable.
However, this does not necessarily mean the data is gone. Since file content often remains in the data area, recovery is frequently possible as long as clusters have not been reused.
Safe Recovery from FAT File System Storage
If access problems occur, a careful approach reduces the risk of permanent loss.
First, stop using the device to prevent overwriting available clusters.
Next, avoid reformatting unless recovery is complete.
Then, use a professional tool such as Magic Data Recovery, which scans FAT-based volumes in read-only mode and reconstructs file chains using remaining table and directory information.
This method aligns with professional data recovery practices and preserves data integrity.
Conclusion
The FAT file system remains relevant because it solves a specific problem: simple, universal data access. Understanding its structure and limitations helps prevent misuse and guides safe recovery when issues arise. If there is unexpected data loss, download Magic Data Recovery to restore files from FAT-based storage safely and professionally.
Supports Windows 7/8/10/11 and Windows Server
FAT File System – FAQ
1.What is the FAT file system?
2.Why is FAT still used today?
3.What is the main limitation of FAT32?
4.Is exFAT the same as FAT?
5.Can FAT storage become corrupted easily?
6.Can files be recovered from a damaged FAT volume?
7.When should FAT not be used?
Vasilii is a data recovery specialist with around 10 years of hands-on experience in the field. Throughout his career, he has successfully solved thousands of complex cases involving deleted files, formatted drives, lost partitions, and RAW file systems. His expertise covers both manual recovery methods using professional tools like hex editors and advanced automated solutions with recovery software. Vasilii's mission is to make reliable data recovery knowledge accessible to both IT professionals and everyday users, helping them safeguard their valuable digital assets.