The Ultimate Guide to Flash Card Memory Reader

We’ve all been there. You return from an incredible vacation or finish a crucial photoshoot, ready to transfer hundreds of photos and videos to your computer. You insert your SD card or microSD card, and… nothing happens. Your computer doesn’t recognize it. A wave of panic hits as you realize your irreplaceable memories or critical work files might be locked away on that tiny piece of plastic. Often, the problem isn’t the card itself, but the bridge between the card and your computer: the flash card memory reader.
This comprehensive guide dives deep into the world of flash card reader technology. We’ll explore how they function, what to look for when buying one, and best practices for safe data transfer. More importantly, we’ll address the dreaded scenario of data loss and provide a reliable solution for recovery. Understanding your tools is the first step in preventing digital disasters and ensuring your data remains secure.
Table of Contents
What is a Flash Card Memory Reader? The Unsung Hero of Data Transfer
A flash card reader is a hardware device that facilitates access to the data stored on flash memory cards. Think of it as a translator and a bridge. Your computer’s operating system speaks a certain language (like USB protocol), while your SD, CFexpress, or Memory Stick card speaks another. The memory card reader interprets these languages, allowing for seamless data transfer, file management, and backup.
Without a reliable reader, even the fastest, most expensive flash card is useless for getting data onto your computer for editing, sharing, or safekeeping. These devices are critical for photographers, videographers, drone pilots, and anyone who uses digital cameras, action cams, or mobile devices with expandable storage.
How Does a Card Reader Actually Work?
Choosing the Best Flash Card Reader: A Buyer’s Guide
Selecting the right reader is not a one-size-fits-all decision. The wrong choice can lead to frustratingly slow transfers or, worse, corruption. Here are the key factors to consider, grounded in industry best practices and common user experience.
Key Factors to Consider
- Compatibility and Supported Formats: This is the most crucial starting point. A quality multi-card readershould support all the formats you use. Common formats include:
- SD, SDHC, SDXC, SDUC
- microSD, microSDHC, microSDXC
- CFexpress Type A/B, CompactFlash (CF)
- Memory Stick, XQD (increasingly rare)
Always check the product specifications against your cards’ labels.
- Connection Interface and Speed: The reader’s connection port determines its maximum potential speed.
- USB 3.2 Gen 1 (formerly USB 3.0): Offers speeds up to 5 Gbps. A good, modern standard for most users.
- USB 3.2 Gen 2 / USB-C: Offers speeds up to 10 Gbps or 20 Gbps (Gen 2×2). Essential for professionals using CFexpress or high-end UHS-II SD cards.
- Thunderbolt 3/4: The premium choice for maximum speed (up to 40 Gbps) on modern Macs and PCs, ideal for 8K video workflows.
Remember, your reader’s speed, your card’s speed, and your computer’s port must all align to achieve the fastest performance.
- Build Quality and Design: Look for readers with sturdy, durable housings. A loose or flimsy port can damage your card’s contacts. Good readers often have non-slip feet and clear labeling. For portability, compact, bus-powered designs are excellent for on-the-go use.
- Single vs. Multi-Slot Readers: A single-slot reader is compact and often very fast for one specific card type. A multi-card reader offers incredible convenience if you handle multiple formats, allowing you to access several cards simultaneously as separate drives.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Bottlenecking Speeds: Pairing a UHS-II SD card with a reader that only supports the older UHS-I standard will drastically slow down your transfers.
- Ignoring Driver Needs: While most are plug-and-play, some advanced readers (especially for CFexpress) may require a driver for optimal performance on certain operating systems. Always check the manufacturer’s website.
- Using Cheap, Unbranded Readers: These can be tempting, but they frequently lack proper shielding, stable controllers, and safety features, increasing the risk of data corruption during transfer.
The Critical Link: How Your Reader Affects Data Safety
Your choice and use of a memory card reader directly impact the integrity of your data. A faulty or low-quality reader is a common, yet often overlooked, cause of data loss.
Typical Data Loss Scenarios Involving Readers
- Sudden Disconnection: Pulling out the reader or card during an active file transfer can corrupt the file being written and potentially damage the card’s file system.
- Physical Damage to the Reader: A damaged USB port or internal connector can create an intermittent connection, leading to read/write errors.
- Incompatibility Issues: A reader that doesn’t fully support a card’s protocol may incorrectly write data, making files unreadable.
- Reader Controller Failure: If the reader’s controller chip malfunctions, it may send incorrect voltages or signals to the card, causing logical damage.
Best Practices for Safe Data Handling
- Always Eject Properly: Use your operating system’s “Eject” or “Safely Remove Hardware” function before physically disconnecting the reader.
- Use a Reliable Power Source: When using a portable reader with a laptop, ensure the laptop is charged or plugged in to prevent a power interruption.
- Maintain Your Reader: Keep the reader’s ports clean and free of dust. Store it in a protective case when not in use.
- Implement a Redundant Workflow: This is the golden rule. Never use a single card as your only storage. Transfer files to your computer and immediately back them up to an external drive or cloud service. A reader is a transfer tool, not a backup solution.
When Disaster Strikes: Recovering Lost Data from Flash Cards
Despite all precautions, data loss can still occur. The card might become unrecognizable, files may appear deleted, or you might get a prompt to format the card. In these moments, it’s vital to stop using the card immediately to prevent overwriting the lost data.
Why Standard Fixes Often Fail
Users often try built-in tools like chkdsk on Windows or First Aid on Disk Utility (Mac). While these can fix minor file system errors, they are also designed to restore “functionality” to a drive, which can sometimes mean deleting corrupted data they can’t understand. For precious photos and documents, this aggressive approach can be counterproductive. You need a tool focused on data recovery, not just disk repair.
Introducing a Professional Recovery Solution
If you find yourself facing data loss after a failed transfer or reader error, specialized software can be your best chance. This is where a dedicated data recovery tool becomes indispensable. These applications are designed to perform deep scans of the storage media, looking for recoverable file signatures and reconstructing lost directory structures without causing further damage.
Recovering Your Files with Magic Data Recovery
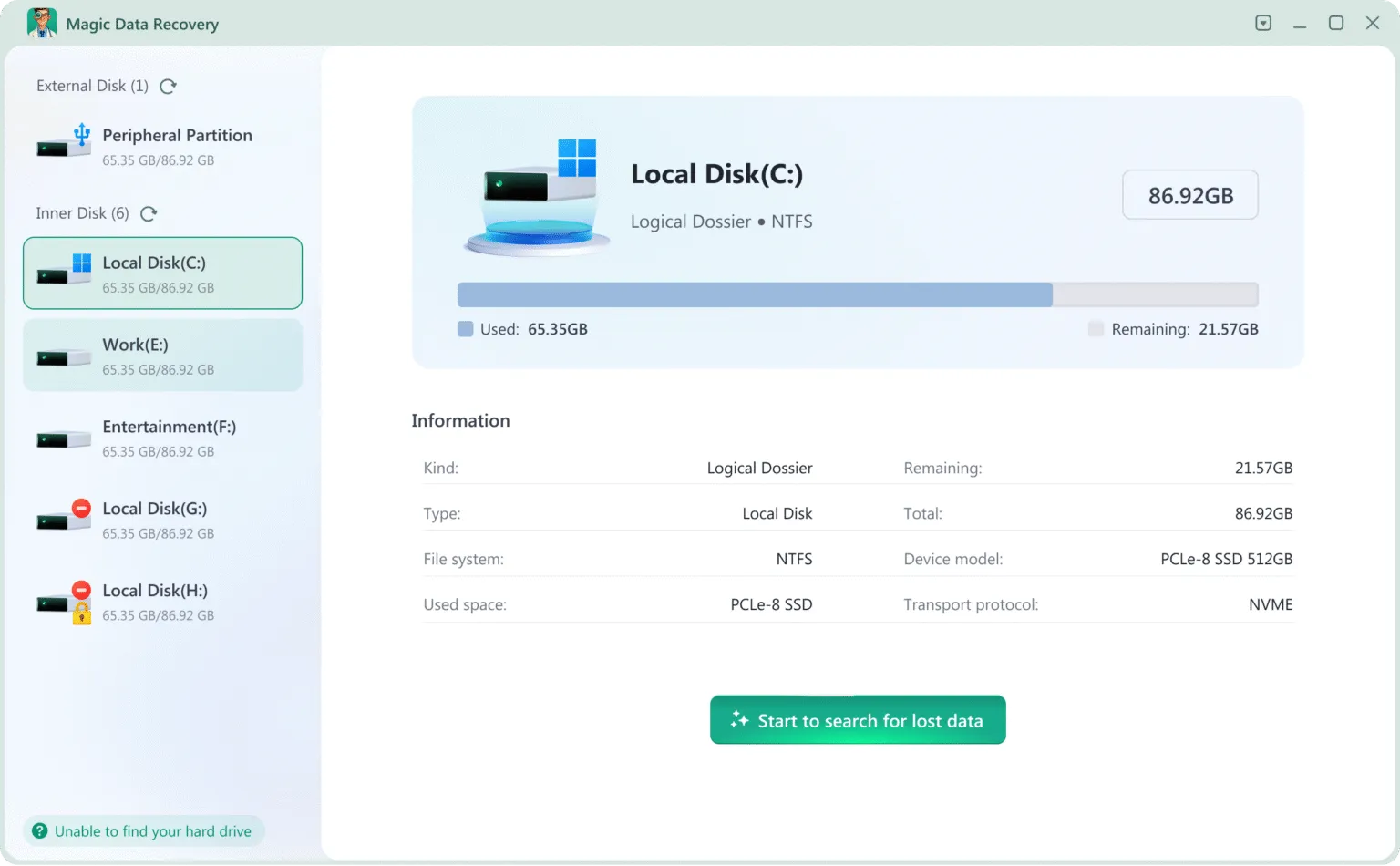
Core Advantages and How It Works
Magic Data Recovery stands out for its user-focused design and powerful scanning engine. Its key advantages include:
- Broad Format Support: It can recover data from all common flash card formats (SD, microSD, CF, etc.) as well as hard drives, SSDs, and USB drives.
- Deep Scan Technology: The software goes beyond simple file table lookup. It performs a thorough sector-by-sector scan to find fragments of lost files, which is crucial for recovering data from formatted or severely corrupted cards.
- Preview Before Recovery: This critical feature allows you to see thumbnails of recoverable photos and documents before you purchase the software. You can verify the file integrity, ensuring the recovery will be successful.
- User-Friendly Interface: The step-by-step wizard guides you through the entire process—selecting the drive, choosing scan type, previewing files, and executing the recovery—making it accessible to non-technical users.
A Typical Recovery Scenario
Imagine your camera’s SD card fails after a transfer via your flash card reader. Your computer asks you to format it. Instead of formatting, you:
- Remove the card and connect it directly via a trusted reader.
- Download and install Magic Data Recovery.
Supports Windows 7/8/10/11 and Windows Server
3. Select the card’s drive letter and click “Search for lost data” to find your lost files.
4. After the scan, you browse the found files, using the preview pane to check your most important JPEG and RAW photos.
5. You select the intact files and recover them to a different drive on your computer (never back to the same card).
This process minimizes risk and maximizes the chance of getting your memories back. Magic Data Recovery offers a more reliable and safer approach than DIY command-line tools or freeware with limited capabilities. Its focused functionality on file recovery makes it a trustworthy tool in your digital toolkit.
Conclusion
A flash card memory reader is far more than a simple dongle; it’s a vital component in your digital workflow. Investing in a high-quality, compatible reader is an investment in the safety of your data. Remember the best practices: eject safely, maintain your gear, and, most importantly, always maintain multiple backups.
However, even with the best habits, technology can fail. When faced with unexpected data loss from a flash card, avoid panic and refrain from using the card further. Employ a specialized tool designed for this precise problem. For a streamlined, effective recovery process that gives you control and visibility, consider using Magic Data Recovery. Its ability to preview files and perform deep scans makes it a sensible choice for recovering what matters most.
Protect your digital legacy. Choose your reader wisely, back up diligently, and know that a powerful recovery solution is available if you need it.
Supports Windows 7/8/10/11 and Windows Server
FAQs
1. What is a flash memory card reader?
2. Can you recover deleted files from a SD card?
3. How to recover deleted files from SD card in Linux?
4. How can I read my SD card?
5. How to use a flash card reader?
6. Are pictures permanently deleted from SD card?
7. How to retrieve data from a memory card?
8. What is the lifespan of an SD card?
Jason has over 15 years of hands-on experience in the computer data security industry. He specializes in data recovery, backup and restoration, and file repair technologies, and has helped millions of users worldwide resolve complex data loss and security issues.



