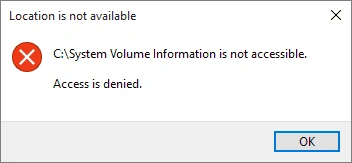
Access Denied Error Meaning & Fixes

The Access Denied message appears when Windows or another system blocks your attempt to open, modify, or move a file, folder, drive, or webpage. Essentially, it signals a restriction based on permissions, ownership, encryption, or security policies.
While it may seem alarming, the error usually does not indicate permanent data loss. Understanding its causes allows you to troubleshoot effectively and regain access safely without compromising your system or files.
Table of Contents
Common Causes of Access Denied
1. Insufficient Permissions
If your account lacks the required rights, Windows will prevent any action on the resource. This is common in shared computers, company networks, or when accessing files transferred from other user accounts.
Tip: Check the account type and request appropriate permissions. Avoid granting full access to everyone, which can compromise security.
2. Ownership Conflicts
Files copied from another PC, account, or system may retain ownership metadata from the original environment. If your account is not recognized as the owner, Windows will deny access.
Solution: Changing ownership to your account can resolve the issue (details below in the Fix section). Always double-check that you are not altering system-critical files.
3. Encryption Requirements
Encrypted files and drives, such as BitLocker-protected volumes, require proper authentication to open. Without the correct key or certificate, Windows will block access immediately.
Tip: Keep recovery keys securely stored. Attempting unauthorized access may trigger security alerts or lock the drive further.
4. Corrupted File System Attributes
NTFS metadata can become corrupted due to improper shutdowns, sudden power loss, or hardware issues. In such cases, even healthy files may appear restricted, producing the Access Denied message.
Solution: File system repair commands or professional recovery tools can often fix these errors without data loss.
5. Security Software Interference
Antivirus or endpoint protection programs occasionally block legitimate file changes to prevent perceived threats. While temporary, these restrictions can trigger access is denied messages.
Tip: Pause real-time protection briefly to test access, but remember to reactivate it afterward.
Step-by-Step Ways to Fix Access is Denied Error
1. Adjust Permissions
① Right-click the file or folder.
② Choose Properties → Security.
③ Select your account and enable Full Control or Modify.
④ Confirm changes and retry accessing the resource.
This is the most common fix and usually resolves permission conflicts.
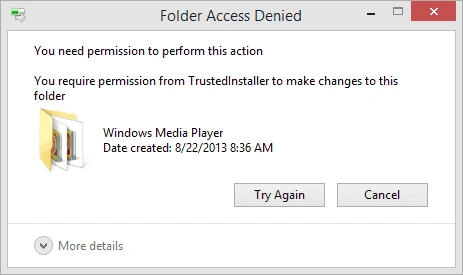
2. Take Ownership
If your account is not recognized as the owner:
① Open Properties → Security → Advanced.
② Click Change next to the Owner field.
③ Enter your username and check Replace owner on subcontainers and objects.
④ Apply changes and retry access.
Warning: Avoid changing ownership of system-critical folders, as this can affect other users or system stability.
3. Close Processes That Lock the File
Some files remain in use by background programs. To fix this:
① Close related applications.
② Restart File Explorer or your computer.
③ Use Task Manager to end processes locking the file.
This step often resolves temporary access issues without changing permissions.
4. Repair File System Errors
Run the following command in an elevated Command Prompt:
chkdsk X: /f
Replace X with the drive letter. This fixes corrupted metadata or file system inconsistencies that trigger access deniedmessages.
Tip: Back up important files before running chkdsk, especially on drives showing signs of failure.
5. Review Security or Antivirus Restrictions
① Temporarily pause your antivirus or endpoint protection to test whether it is causing the block.
② Retry accessing the file or folder.
③ Re-enable protection immediately after testing.
Avoid leaving security software disabled for long periods to prevent vulnerabilities.
6. When the Problem Involves Data Loss
If a drive is damaged, RAW, or unreadable, the message may appear despite correct permissions. Instead of formatting:
① Use a professional, read-only recovery tool to retrieve data.
② Avoid writing new data to the affected drive to prevent permanent loss.
Tools like Magic Data Recovery allow you to recover files safely before applying repairs.
Conclusion
The Access Denied or Access is Denied error is typically caused by permission conflicts, ownership issues, encryption, or corrupted file system attributes. Most cases can be resolved safely using the steps outlined above.
Always prioritize data safety: back up important files, avoid unnecessary permission changes, and use read-only recovery tools if drives show signs of damage. Following these precautions ensures your files remain protected while restoring access. Here is the download button of Read-Only data recovery tool.
Supports Windows 7/8/10/11 and Windows Server
Access Denied FAQs
What causes Windows to block access to a folder?
Can file system corruption cause Access Denied?
How do I check the owner of a file?
Does encryption prevent access?
Why does antivirus block file changes?
Can restarting the PC resolve Access Denied?
What should I do before repairing a damaged drive?
How can I distinguish between permission issues and file corruption?
Is it safe to change ownership on system files?
How can I prevent future Access Denied errors?
Erin Smith is recognized as one of the most professional writers at Amagicsoft. She has continually honed her writing skills over the past 10 years and helped millions of readers solve their tech problems.