Understanding the NTFS Master File Table (MFT)
NTFS Master File Table (MFT) is a key component of the NTFS (New Technology File System), the default file system for Windows operating systems. It serves as the backbone of NTFS and stores essential information about files and directories on the disk. The MFT contains metadata such as file names, sizes, creation dates, and locations, allowing the operating system to quickly access and manage files.
In this article, we’ll explore the structure of the NTFS Master File Table, how it functions, and common issues such as a corrupt MFT. We’ll also cover frequently asked questions to help you understand this crucial part of the NTFS file system.
Table of Contents
What is the Master File Table (MFT)?
NTFS Master File Table (MFT) is a database that contains records for every file and directory on an NTFS volume. Each MFT record represents a file or directory. It stores metadata such as the file name, size, creation date, and data location.
Unlike older file systems such as FAT32 or ExFAT, which rely on a File Allocation Table (FAT), NTFS uses the MFT to manage information for every file. The MFT allows for more efficient file access and management, as it contains all the data the operating system needs to retrieve files quickly.
Every file and directory has an entry in the MFT. This includes system files. Even special files like $MFT and $LogFile are stored in the MFT. The MFT also handles metadata for small files and directories, as well as file system-level data like security descriptors and file permissions.

How the MFT Works in NTFS
In NTFS, the system represents every file with an MFT record. Each record is made up of multiple attributes that describe the file, such as:
- File Name: The file’s name and path.
- Data: The actual data or content of the file.
- Attributes: Information like file size, timestamps (creation, modification), and access control information.
- File Location: The location of the file’s data on the physical disk, typically as a cluster or block of sectors.
- Security Descriptors: Access control information that defines which users or groups have permission to access the file.
The MFT improves access speed compared to older file systems. It centralizes file information in a table, which helps the operating system locate files faster. It also optimizes disk space usage by storing small files directly in the MFT, reducing fragmentation.
Where is the Master File Table Stored in NTFS?
NTFS stores the MFT directly on the volume, usually near the beginning of the disk in a designated system area. It’s usually located near the start of the partition, in a reserved area called the MFT zone, which ensures that the system can access it quickly.
The MFT is replicated several times across the disk for redundancy. NTFS creates backup copies of the MFT in case the primary copy becomes damaged. NTFS stores these backups at specific disk locations. This design helps recover data if corruption occurs.
Repairing a Corrupt MFT
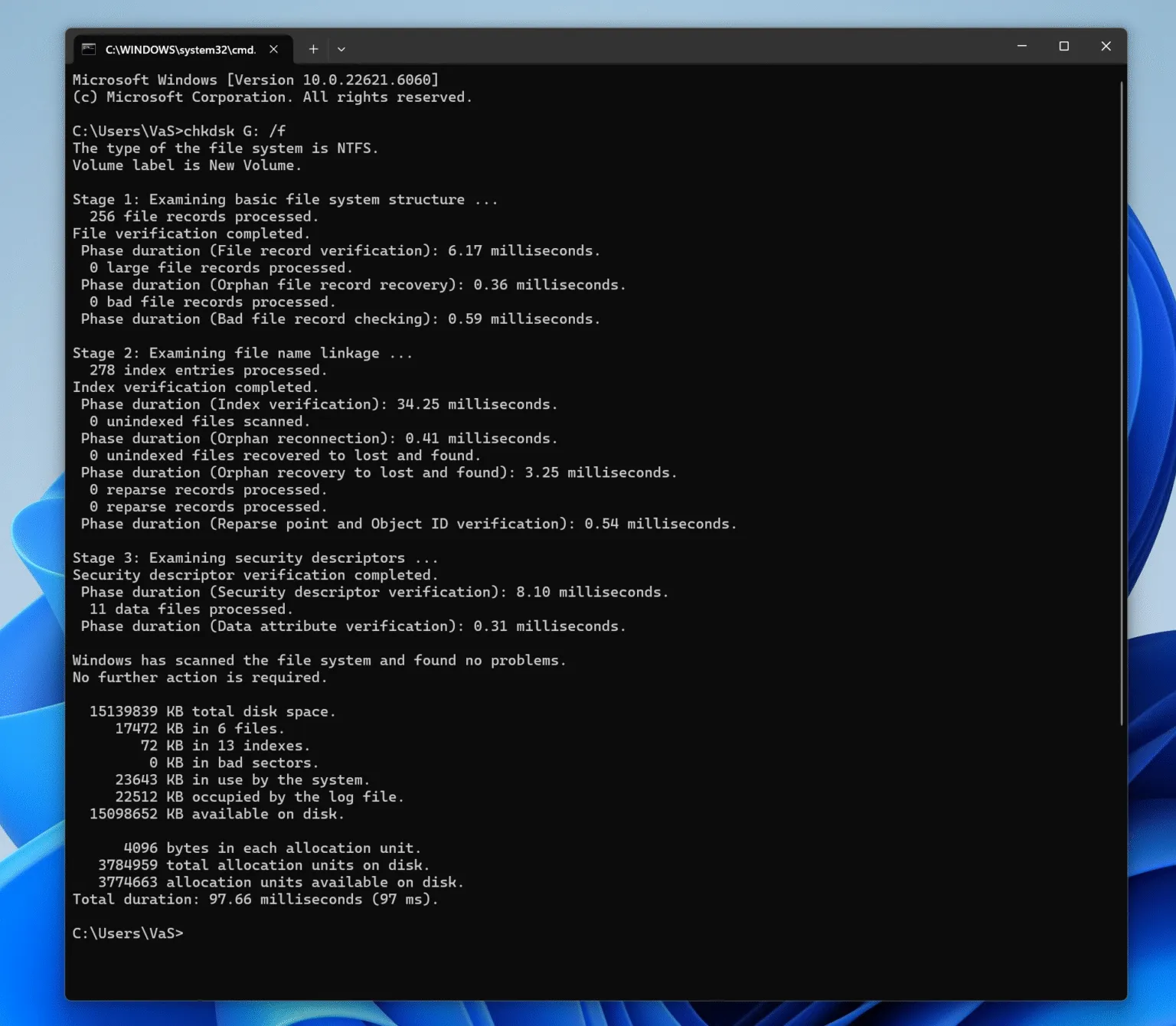
A corrupt NTFS Master File Table (MFT) can lead to serious data access issues. Files may become inaccessible, and the system may fail to boot. If the MFT is corrupt, the first step is to try repairing it using chkdsk (Check Disk), a built-in Windows utility designed to fix file system errors. Here’s how to run chkdsk:
1. Open Command Prompt with administrative privileges.
2. Type chkdsk X: /f (replace X with the drive letter you want to check).
3. Press Enter and allow the tool to scan and attempt to repair any file system errors.
In some cases, third-party tools such as Magic Data Recovery can help recover data from a volume with damaged MFT.
Conclusion
NTFS Master File Table (MFT) is a fundamental component of the NTFS file system, managing all file metadata and improving the efficiency of file storage and retrieval. Understanding the MFT and its role helps you manage NTFS volumes more effectively. It also helpful with troubleshooting and data recovery. Provided the MFT becomes corrupt, tools like chkdsk and a professional data recovery tool can help you repair or recover data from the disk. If you are looking for this kind of a tool, Magic Data Recovery can help you recover data from NTFS drives, even if the NTFS Master File Table is corrupted or damaged.
Supports Windows 7/8/10/11 and Windows Server
NTFS Master File Table – FAQ
1.Where is the master file table stored in NTFS?
2.Does NTFS have a file allocation table?
3.How to repair a corrupt master file table?
4.How do you view the MFT table?
5.What is a master file table?
6.Can an NTFS USB drive be bootable?
7.How does the master file table handle small files in NTFS?
8.Where is the File Allocation Table located?
Vasilii is a data recovery specialist with around 10 years of hands-on experience in the field. Throughout his career, he has successfully solved thousands of complex cases involving deleted files, formatted drives, lost partitions, and RAW file systems. His expertise covers both manual recovery methods using professional tools like hex editors and advanced automated solutions with recovery software. Vasilii's mission is to make reliable data recovery knowledge accessible to both IT professionals and everyday users, helping them safeguard their valuable digital assets.



