A Practical Guide to Encrypting File System

Protecting sensitive files has become a necessity rather than a choice. As digital documents continue to grow in volume and value, the risk of unauthorized access also increases. From personal records to confidential work files, unprotected data can be exposed through device loss, account misuse, or simple human error. This is exactly where an encrypting file system becomes relevant.
In this guide, you will learn what is encrypting file system, how it works in real-world Windows environments, and why it matters for everyday users. More importantly, the article explains practical benefits, realistic limitations, and common mistakes to avoid. By the end, you will be able to decide whether an encrypting file system fits your data protection needs and how to prepare for unexpected data loss scenarios.
Table of Contents
What Is an Encrypting File System?
EFS is a file-level encryption feature built into certain file systems, most notably for NTFS. It allows users to encrypt individual files or folders so that only authorized accounts can read the data.
Instead of encrypting an entire drive, an encrypting file system focuses on specific files. Once enabled, the NTFS file system automatically encrypts files when saving them and decrypts them when an authorized user opens them. Because this process runs in the background, users do not need to manage encryption manually.
For users asking what is encrypting file system in practical terms, it is a built-in method to protect files by linking encryption access directly to a user account.
How Does Encrypting File System Work?
To understand the value of an encrypting file system, it helps to see how the encryption process actually works. EFS combines security and performance by using more than one encryption method.
File-Level Encryption Explained
First, EFS generates a unique file encryption key (FEK) for each file. Next, the system uses this key to encrypt the file contents. After that, EFS encrypts the FEK itself using the user’s public key. As a result, only the matching private key can unlock the file.
This layered approach allows an encrypting file system to stay secure without slowing down everyday file access.
The Role of Certificates in EFS
Encryption certificates play a critical role in EFS. If a user deletes an account, reinstalls Windows, or loses the user credentials, access to encrypted files may stop completely. For this reason, backing up encryption certificates is considered a best practice rather than an optional step.
Encrypting File System and NTFS: What Is the Relationship?
An encrypting file system like EFS depends entirely on NTFS. Without NTFS, EFS cannot operate.
NTFS is a file system that handles file structure, permissions, and access control. On top of that foundation, EFS applies encryption to protect file contents. In other words, NTFS manages how files exist on the disk, while EFS controls who can read them.
Because of this close relationship, users must confirm that a drive uses NTFS before enabling an encrypting file system.
Common Use Cases for Encrypting File System
EFS is most useful in scenarios such as:
- Protecting personal documents on shared computers
- Securing business files on employee workstations
- Preventing unauthorized access after device theft
For individual files that require confidentiality, EFS offers a lightweight and integrated solution.
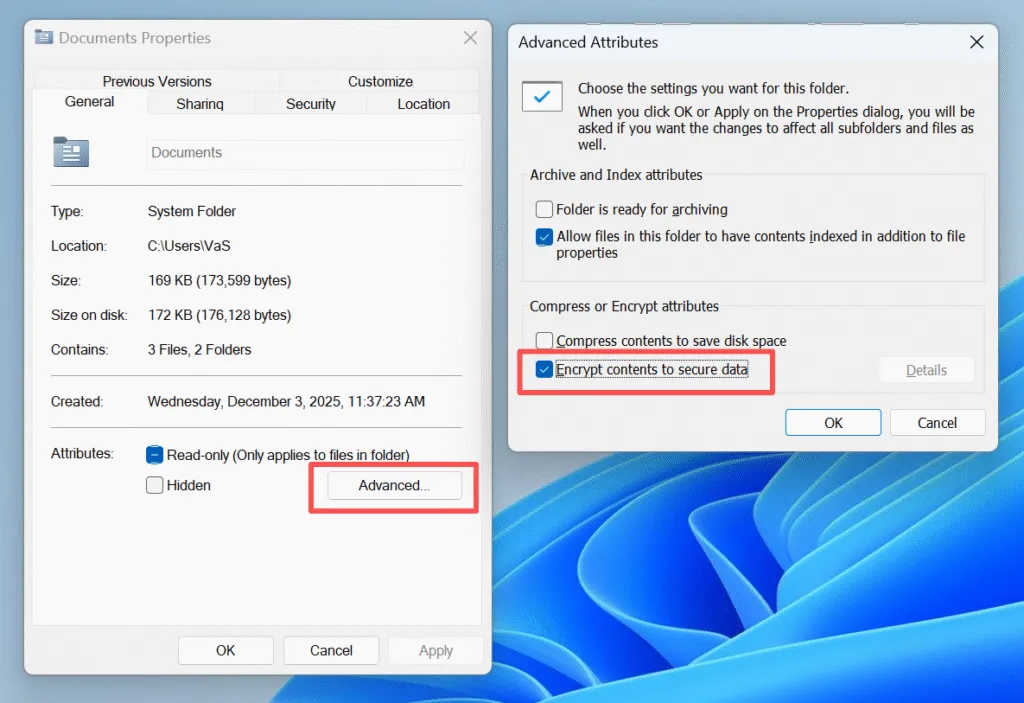
Types and Methods of Encryption Explained
Encryption can be implemented in different ways depending on the use case.
Four Common Types of Encryption
- File-level encryption (EFS)
- Full-disk encryption (such as BitLocker)
- Database encryption
- End-to-end encryption for communications
Three Main Encryption Methods
- Symmetric encryption
- Asymmetric encryption
- Hybrid encryption
Most modern systems, including an encrypting file system, use a hybrid approach to balance security and performance.
Downsides and Limitations of Encryption
Although encryption strengthens data protection, it also introduces trade-offs that users should understand.
First, losing certificates can permanently block access to files. Second, encrypted files often become inaccessible when moved to unsupported systems. Finally, encryption complicates recovery efforts if users do not plan ahead.
Therefore, anyone using an encrypting file system should combine encryption with backups and a clear recovery strategy.
Can Encrypted Files Be Recovered From Encrypting File System?
Recovery depends on the situation. If encrypted files are deleted or lost due to file system failure, recovery is possible only if the user credentials still exist. Encryption does not destroy data, but it does restrict access. This is where a reliable data recovery solution becomes important.
How Magic Data Recovery Helps When Encrypted Files Are Deleted
It is important to clarify the role of data recovery tools in encrypted environments. Magic Data Recovery does not decrypt encrypted files or repair inaccessible encrypted files. Encryption must be properly removed or unlocked by the user before any file access is possible.
However, Magic Data Recovery can still be useful in specific and legitimate scenarios related to an encrypting file system, particularly when encrypted files are deleted.
Magic Data Recovery is suitable when:
- Encrypted files were deleted by mistake, but the encryption was previously valid
- Files were removed from an NTFS drive using EFS and the correct user credentials still exist
- The storage device itself is healthy and accessible after decryption or unlocking
Key strengths include:
- Focus on recovering deleted files although the file is encrypted
- Read-only scanning that does not alter original data
- Support for common file systems
Compared with attempting manual recovery methods, this approach reduces the risk of further data loss while staying within proper security boundaries.
Conclusion
An encrypting file system offers a practical way to protect sensitive files, especially on Windows systems that support EFS. By encrypting files at the user level, it helps prevent unauthorized access without adding daily complexity.
At the same time, encryption alone is not enough. Users must manage certificates carefully and prepare for situations where files are deleted, formatted or systems fail. If you have the password or credentials, Magic Data Recovery can be a practical option for the lost encrypted files.
Supports Windows 7/8/10/11 and Windows Server
FAQs About Encrypting File System
What is an encrypting file system?
What is the best way to encrypt a file?
What is EFS and NTFS?
What are the four types of encryption?
Which software is best for file encryption?
What are the downsides of encryption?
What are the three methods of encryption?
How much does encryption cost?
Vasilii is a data recovery specialist with around 10 years of hands-on experience in the field. Throughout his career, he has successfully solved thousands of complex cases involving deleted files, formatted drives, lost partitions, and RAW file systems. His expertise covers both manual recovery methods using professional tools like hex editors and advanced automated solutions with recovery software. Vasilii's mission is to make reliable data recovery knowledge accessible to both IT professionals and everyday users, helping them safeguard their valuable digital assets.