How to Check Hard Disk Errors: A Complete Guide

Hard disk errors can cause major issues, including data corruption, system crashes, and slow performance. Whether you’re experiencing unusual system behavior or simply want to check the health of your hard drive, knowing how to check hard disk errors is crucial for data security. Fortunately, there are several methods available to scan for and repair hard drive problems using built-in Windows tools and third-party software.
In this guide, we’ll explain how to check hard disk errors, walk you through troubleshooting steps, and show you how to keep your drive in top condition.
Table of Contents
What Are Hard Disk Errors?
Hard disk errors are problems that affect the physical or logical functioning of your hard drive. These errors can arise from various causes, including bad sectors, file system corruption, or even hardware failure. If left unchecked, these errors can lead to data loss, system instability, and potential drive failure.
Some common types of hard disk errors include:
- Bad sectors: Damaged or unreadable portions of the disk.
- File system corruption: When the file structure is damaged, leading to data inaccessibility.
- Drive failure: Complete failure of the disk due to physical damage.
Recognizing and addressing these issues early can help prevent data loss and ensure the longevity of your hard drive.
How to Check for Hard Disk Errors in Windows
Method 1: Using CHKDSK
CHKDSK (Check Disk) is a built-in Windows utility designed to scan and fix file system errors and bad sectors. Here’s how you can use CHKDSK to check for hard disk errors:
1. Open Command Prompt as Administrator:
Type “cmd” in the search bar, right-click on Command Prompt, and select Run as Administrator.
2. Run the CHKDSK Command:
In the Command Prompt window, type the following command and press Enter:
chkdsk X: /f
- X: refers to the drive letter you want to check (replace it if needed).
- The
/fflag tells CHKDSK to fix any errors it finds.
3. Let CHKDSK Scan and Fix Errors:
When you restart your computer, CHKDSK will run automatically and check for errors. The process may take a while depending on the size of your disk.
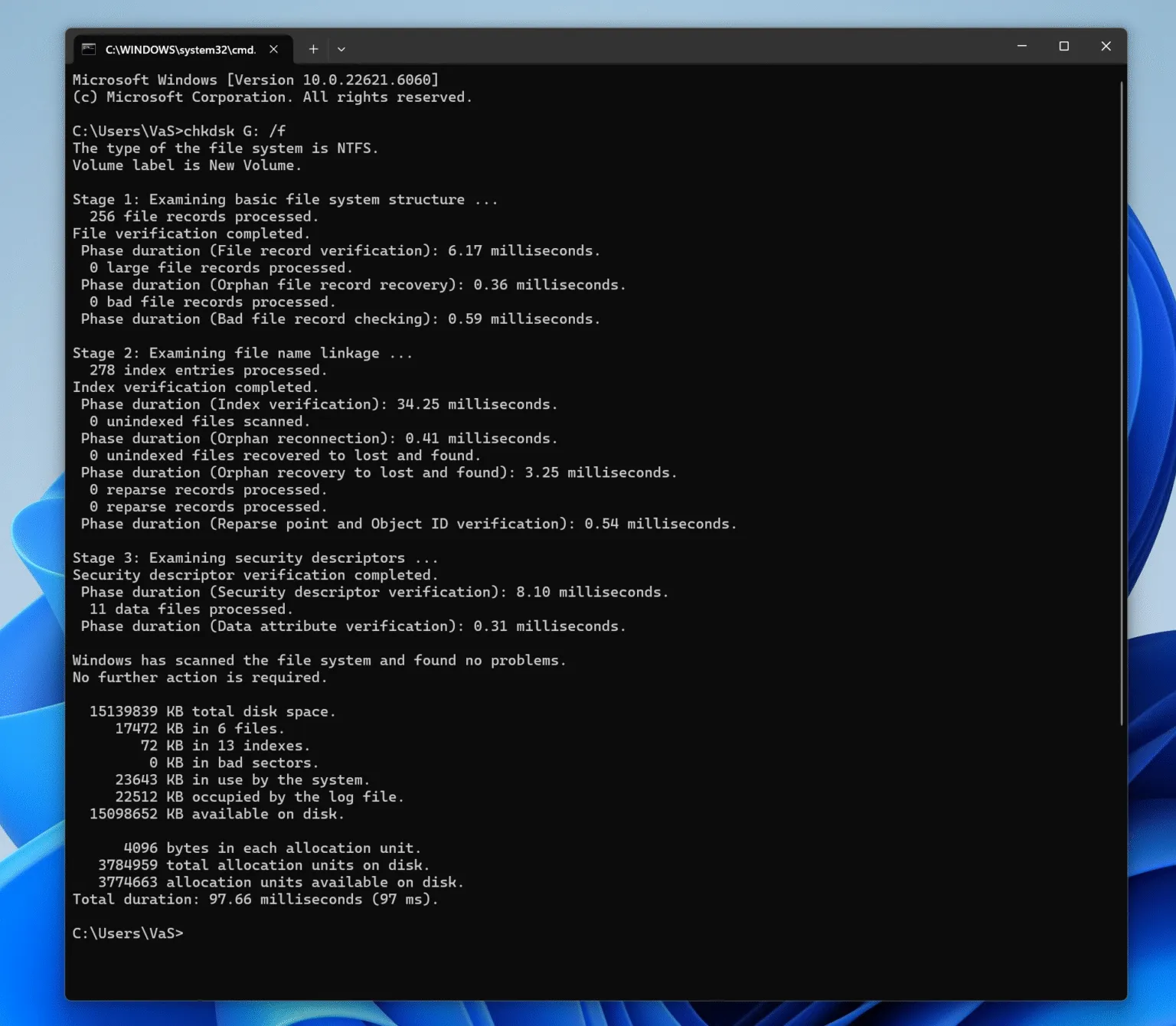
CHKDSK will attempt to fix errors like bad sectors and corrupt file systems. If it finds physical damage, it can’t repair it, but it will mark bad sectors to prevent the system from using them.
Method 2: Using System File Checker (SFC)
System File Checker (SFC) is another Windows tool used to scan and repair corrupted system files, which can sometimes contribute to hard disk errors. Here’s how to run it:
1. Open Command Prompt as Administrator:
Type “cmd” in the search bar, right-click Command Prompt, and choose Run as Administrator.
2. Run the SFC Command:
In the Command Prompt window, type:
sfc /scannow
This will initiate the scan and repair process. It may take some time to complete, so be patient.
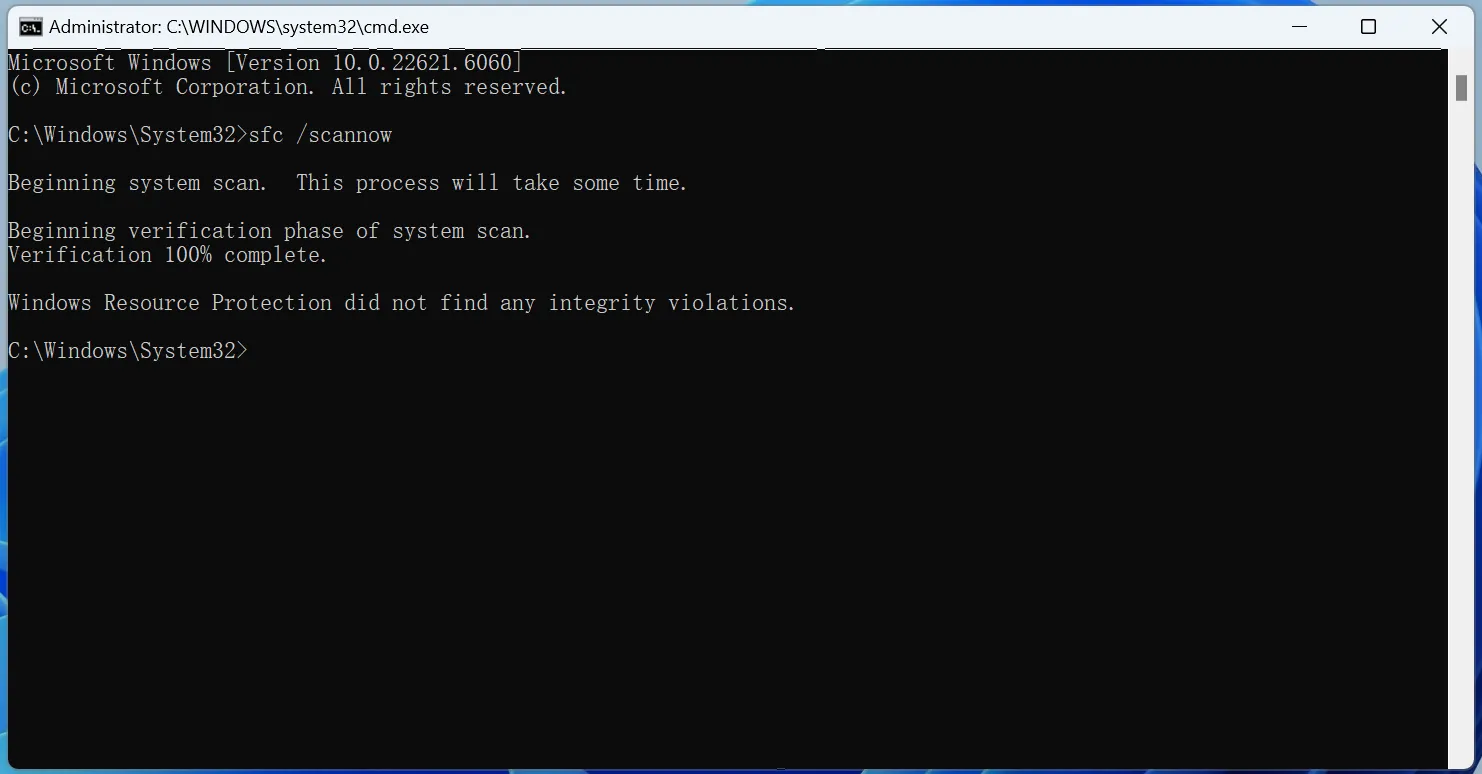
3. Review the Scan Results:
Once the scan finishes, the tool will inform you whether it found any issues and whether it successfully fixed them.
While SFC primarily focuses on repairing corrupted system files, it can help resolve some hard disk errors related to file access.
Method 3: Third-Party Tools for Hard Disk Health Monitoring
In addition to CHKDSK and SFC, third-party software can provide deeper insights into the health of your hard drive. These tools often offer more advanced diagnostics, such as monitoring disk temperature, health status, and the presence of bad sectors.
Some of the best third-party tools for hard disk error detection include:
- CrystalDiskInfo: A free utility that provides detailed information about your hard drive’s health, temperature, and SMART status.
- HD Tune: A reliable tool for scanning and monitoring your hard drive, identifying errors, and checking drive performance.
These tools are especially helpful for diagnosing hard disk problems that CHKDSK and SFC cannot address, such as hardware failure or excessive wear.
How to Fix Hard Disk Errors
Once you’ve identified the issues with your hard disk, there are several ways to address them:
1. Run CHKDSK and SFC: As outlined earlier, using CHKDSK to fix file system errors and SFC to repair system files is often the first step in fixing hard disk problems.
2. Back Up Your Data: If your hard disk shows signs of failure, it’s essential to back up your important data immediately to avoid data loss. Data recovery software like Magic Data Recovery can help retrieve lost data before replacing the drive.
3. Replace the Hard Drive: In cases of physical damage (e.g., bad sectors that cannot be fixed), replacing the hard drive is the safest option.
Conclusion
How to check hard disk errors is vital for maintaining system stability and protecting your data. Tools like CHKDSK and SFC are great first steps for diagnosing and fixing common hard disk issues. For more comprehensive diagnostics, third-party tools like CrystalDiskInfo and HD Tune can help you monitor the overall health of your hard drive.
However, if you’re dealing with a failed or failing hard disk, or if you’re struggling to recover files from a corrupted drive, it’s highly recommended to try Magic Data Recovery. This software is a reliable and efficient solution that helps recover lost data from unrecognized hard drives, making it an ideal tool for addressing data loss during disk failure.
Supports Windows 7/8/10/11 and Windows Server
FAQs – How to Check Hard Disk Errors
How to check hard drive errors?
Is there a free software for HDD testing?
How to check if a hard disk is corrupted or not?
How do I run SFC and CHKDSK?
How to identify a faulty hard drive?
Will CHKDSK fix corrupt files?
Should I run SFC or DISM first?
Vasilii is a data recovery specialist with around 10 years of hands-on experience in the field. Throughout his career, he has successfully solved thousands of complex cases involving deleted files, formatted drives, lost partitions, and RAW file systems. His expertise covers both manual recovery methods using professional tools like hex editors and advanced automated solutions with recovery software. Vasilii's mission is to make reliable data recovery knowledge accessible to both IT professionals and everyday users, helping them safeguard their valuable digital assets.



