File Allocation Table Explained

A file allocation table plays a critical role in how data is stored, located, and accessed on many storage devices. USB flash drives, SD cards, and older hard drives rely on this structure to keep track of where files are physically saved. When the file system structure works correctly, files open instantly and storage appears reliable. However, once it becomes damaged or corrupted, partitions may suddenly turn inaccessible, files may disappear, or the drive may prompt you to format it.
This guide explains how the file allocation table works in real-world usage, why problems occur, and what practical steps users can take when data loss happens. Toward the end, you will also learn what can help recover data when FAT-related issues prevent normal access.
Table of Contents
What Is a File Allocation Table?
A file allocation table (often abbreviated as FAT) is a data structure used by certain file systems to manage how files are stored on a disk. It acts like a map, telling the operating system where each file begins, how many blocks it occupies, and which blocks are linked together.
In simple terms:
- Each file is set up by small units called clusters
- The file allocation table records which clusters belong to which file
- The operating system consults this table whenever a file is opened, modified, or deleted
Because this table is essential for navigation, even minor damage can make large amounts of data appear lost, even though the actual file content still exists on the device.
How File Allocation Tables Work on Common Storage Devices
Different storage devices rely on this file system structure in slightly different ways, but the core concept remains the same.
File Allocation Table on USB Drives and SD Cards
Removable storage devices commonly use FAT-based file systems due to their broad compatibility. Cameras, media players, and embedded devices can all read FAT-formatted media.
Typical scenarios include:
- SD cards used in cameras or drones
- USB flash drives used for file transfer
- External storage shared between different operating systems
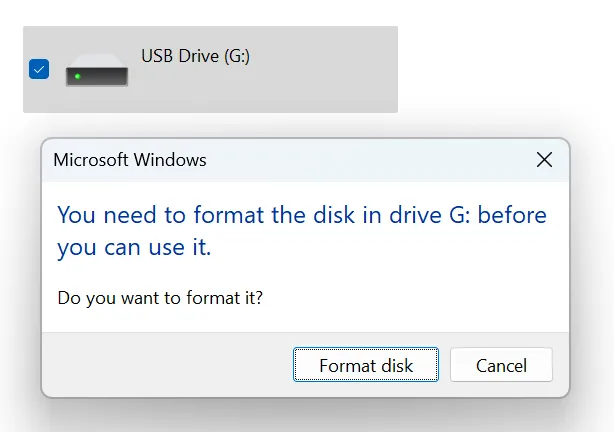
When the FAT structure becomes corrupted on these devices, users often see errors such as “The drive is not accessible” or “You need to format the disk before using it.”
File Allocation Table on External Hard Drives
Some external hard drives, especially older or cross-platform ones, still rely on FAT variants. While these drives can store large files, they are also vulnerable to sudden power loss and unsafe removal, both of which can damage the underlying FAT metadata.
Common Problems Caused by File Allocation Table Corruption
Damage to FAT file system metadata rarely happens without warning. In most cases, it is triggered by usage habits or system-level interruptions.
Common causes include:
- Sudden power failure during file transfer
- Unplugging a drive without safe removal
- File system errors caused by bad sectors
- Malware targeting file system structures
As a result, users may experience:
- Partitions showing as RAW
- Files missing or appearing with incorrect names
- Extremely slow access to stored data
- System prompts asking to format the drive
Can Data Still Be Accessed When the File Allocation Table Is Damaged?
In many cases, yes. Although the FAT index may be unreadable, the actual file data often remains intact on the storage medium. The main issue is that the operating system can no longer locate or interpret that data correctly.
This is why experts strongly advise:
- Stop using the affected device immediately
- Avoid formatting or running aggressive repair tools
- Do not copy new data onto the same drive
These steps reduce the risk of overwriting recoverable files.
How to Recover Data from a Corrupted File Allocation Table
Why Built-in Repair Tools May Not Be Enough
Utilities such as CHKDSK or file system repair tools focus on restoring logical consistency. While they may fix minor errors, they often modify the critical FAT entries directly. This can permanently break file cluster chains and make recovery more difficult.
Repair does not always mean recovery. In many situations, preserving existing data should be the priority.
Using Data Recovery Software for Safe File Extraction
Specialized recovery software works differently. Instead of relying on damaged file system references, it scans the disk at a lower level to identify file signatures and reconstruct lost file structures.
This approach allows users to extract files without altering the original storage device.
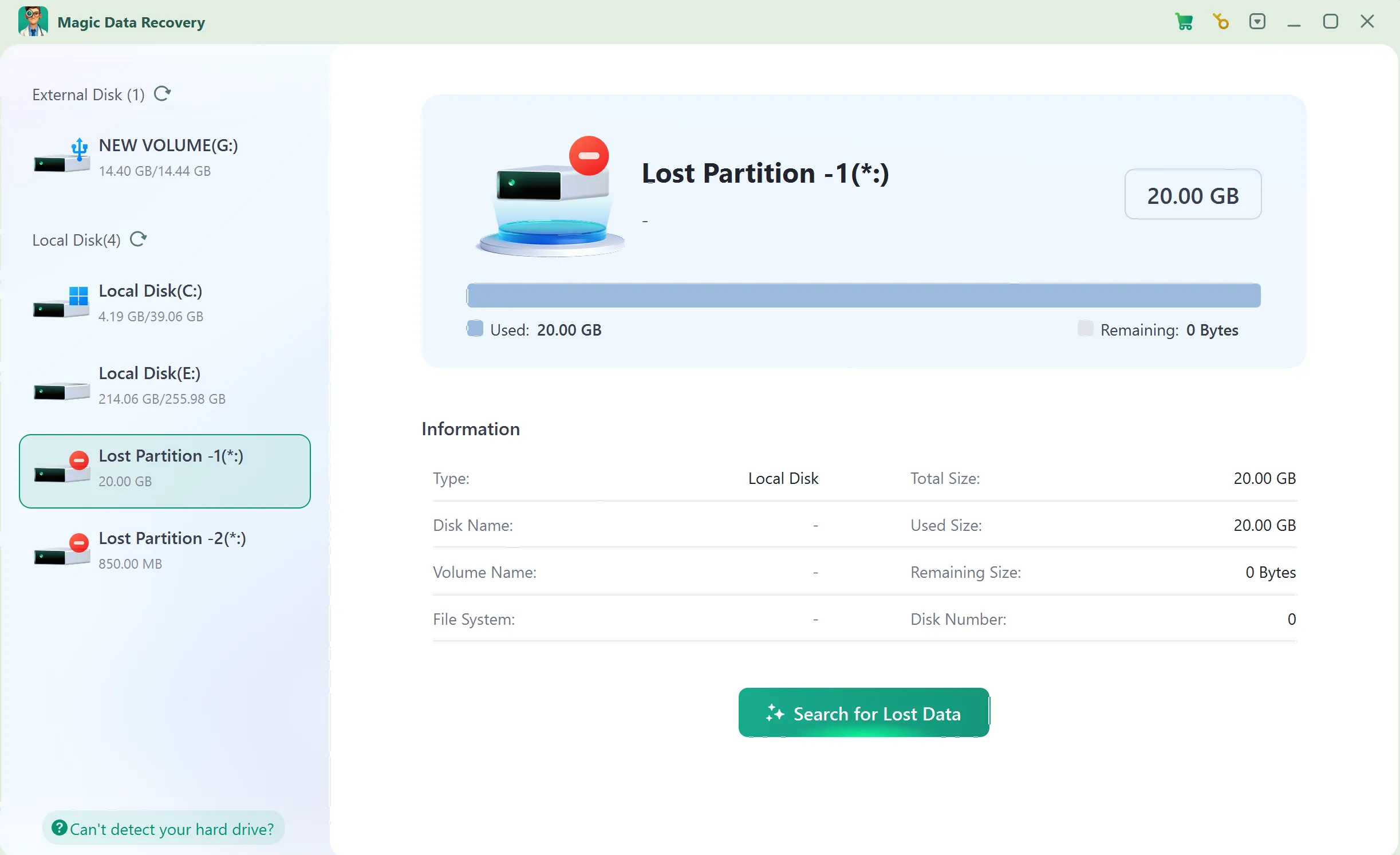
Recommended Solution: Recover Data with Magic Data Recovery
When a FAT-based file system metadata becomes corrupted and access fails, Magic Data Recovery provides a practical solution. It helps users:
- Scan storage devices affected by FAT corruption
- Recover files from inaccessible or RAW partitions
- Preserve original data through read-only scanning
Why Magic Data Recovery Stands Out
Several factors make this tool reliable:
- It avoids modifying the original storage device
- It supports common FAT-based devices
- It offers preview options before file recovery
For example, if an SD card suddenly becomes unreadable due to file allocation table damage, Magic Data Recovery can locate photos and videos even when the system suggests formatting.
Best Practices to Prevent File Allocation Table Damage
Although recovery remains possible, prevention saves time and effort.
To reduce risk:
- Always eject devices safely
- Avoid interrupting file transfers
- Maintain regular backups
- Scan removable media for malware
By adopting these habits, users significantly lower the chance of file system corruption.
Conclusion
The file allocation table remains essential to how many storage devices organize data. When corruption occurs, files may appear lost even though they still exist. By understanding how FAT works and avoiding risky actions, users improve their chances of successful recovery.
In situations involving damaged FAT-based file systems and inaccessible partitions, Magic Data Recovery offers a reliable and careful approach that prioritizes data safety over risky repairs. If you need a focused solution for FAT-related data loss, Magic Data Recovery is worth considering.
Supports Windows 7/8/10/11 and Windows Server
FAQ
What is the file allocation table?
Does NTFS have a file allocation table?
What is file allocation?
Where is the file allocation table stored?
What is File Allocation Table virus?
What are the 4 types of computer files?
Vasilii is a data recovery specialist with around 10 years of hands-on experience in the field. Throughout his career, he has successfully solved thousands of complex cases involving deleted files, formatted drives, lost partitions, and RAW file systems. His expertise covers both manual recovery methods using professional tools like hex editors and advanced automated solutions with recovery software. Vasilii's mission is to make reliable data recovery knowledge accessible to both IT professionals and everyday users, helping them safeguard their valuable digital assets.